
THE HALL EFFECT
 المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
المؤلف:
Donald A. Neamen
 المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
المصدر:
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 177
الجزء والصفحة:
p 177
 20-5-2017
20-5-2017
 2420
2420
THE HALL EFFECT
The Hall effect is a consequence of the forces that are exerted on moving charges by electric and magnetic fields. The Hall effect is used to distinguish whether a semiconductor is n type or p type and to measure the majority carrier concentration and majority carrier mobility. The Hall effect device, as discussed in this section, is used to experimentally measure semiconductor parameters. However, it is also used extensively in engineering applications as a magnetic probe and in other circuit applications.
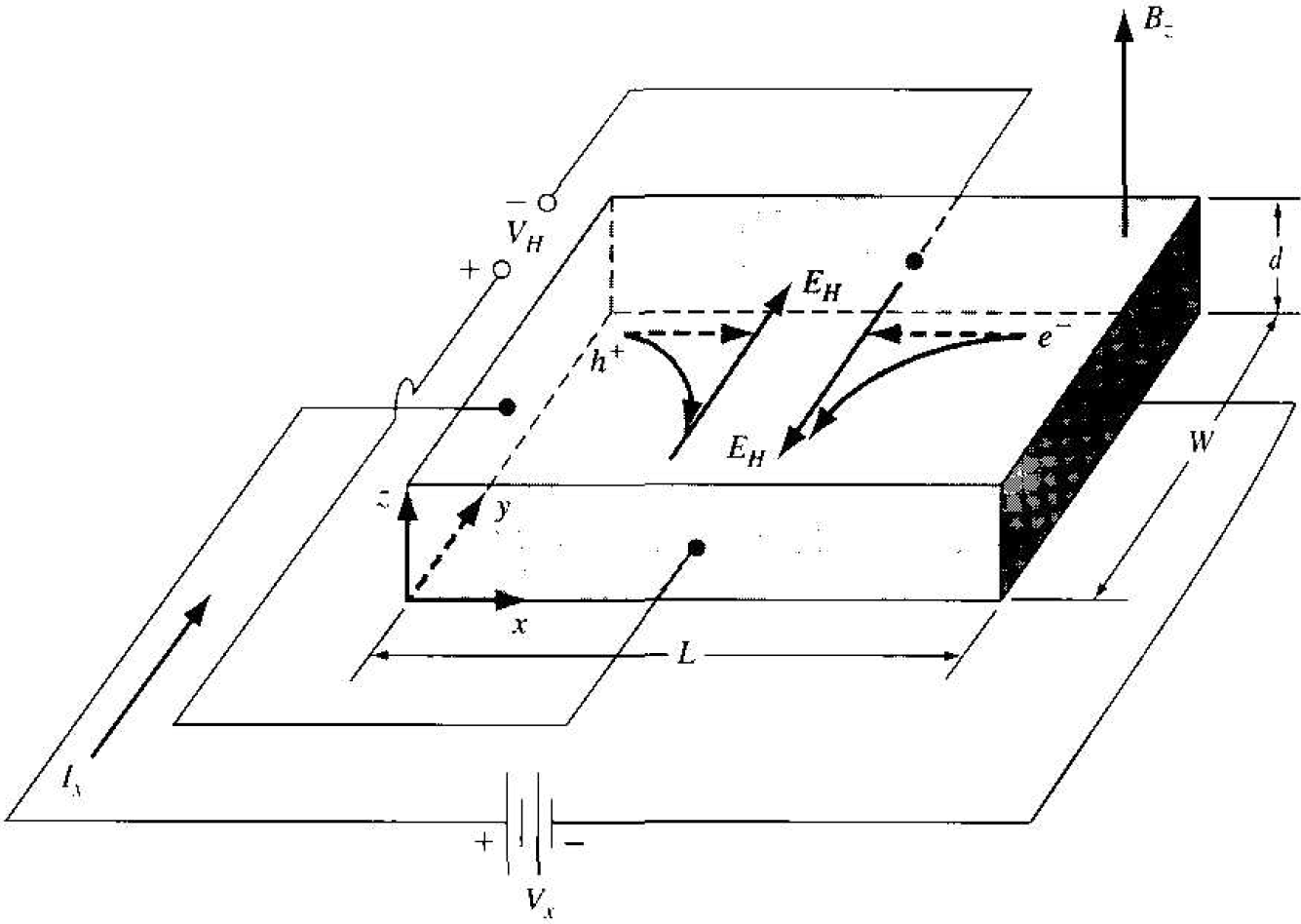
Figure 1.1 Geometry for measuring the Hall effect.
The force on a particle having a charge q and moving in a magnetic field is given by
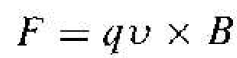 (1)
(1)
where the cross product is taken between velocity and magnetic field so that the force vector is perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field.
Figure 1.1 illustrates the Hall effect. A semiconductor with a current Ix placed in a magnetic field perpendicular to the current. In this case, the magnetic field is in the z direction. Electrons and holes flowing in the semiconductor will experience a force as indicated in the figure. The force on both electrons and holes is in the (-y) direction. In a p-type semiconductor (p0 > n0), there will be a buildup of positive charge on the y = 0 surface of the semiconductor and. in an n-type semiconductor (n0 > P0), there will be a buildup of negative charge on the y = 0 surface. This net charge induces an electric field in the y-direction as shown in the figure. In steady state, the magnetic held force will he exactly balanced by the induced electric field force. This balance may be written as
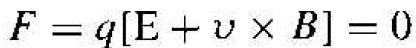 (2a)
(2a)
which becomes
 (2b)
(2b)
The induced electric field in the y-direction is called the Hall field. The Hall field produces a voltage across the semiconductor which is called the Hull voltage. We can write
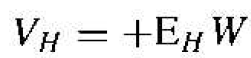 (3)
(3)
The hole mobility is then given by
 (4)
(4)
Similarly for an n-type semiconductor, the low-field electron mobility is determine from
 (5)
(5)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


