
Correction for Buoyancy
 المؤلف:
D. A. Skoog, F. J.Holler, D M. West, and S. R. Crouch
المؤلف:
D. A. Skoog, F. J.Holler, D M. West, and S. R. Crouch
 المصدر:
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry
المصدر:
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
9th. p 23
الجزء والصفحة:
9th. p 23
 16-4-2017
16-4-2017
 2923
2923
Correction for Buoyancy
A buoyancy error will affect data if the density of the object being weighed differs significantly from that of the standard masses. This error has its origin in the difference in buoyant force exerted by the medium (air) on the object and on the masses. Buoyancy corrections for electronic balances6 may be accomplished with the equation where W1 is the corrected mass of the object, W2 is the mass of the standard masses, dobj is the density of the object, dwts is the density of the masses, and dair is the density of the air displaced by masses and object. The value of dair is 0.0012 g/cm3.
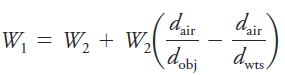 (1.1)
(1.1)
The consequences of Equation 1-1 are shown in Figure 1.1 in which the relative error due to buoyancy is plotted against the density of objects weighed in air against stainless steel masses. Note that this error is less than 0.1% for objects that have a density of 2 g/cm3 or greater. It is thus seldom necessary to correct the masses of most solids. The same cannot be said for low-density solids, liquids, or gases, however. For these, the effects of buoyancy are significant, and a correction must be applied.
The density of masses used in single-pan balances (or to calibrate electronic balances) ranges from 7.8 to 8.4 g/cm3, depending on the manufacturer. Use of 8 g/cm3 is close enough for most purposes. If greater accuracy is required, the manufacturer’s specifications for the balance usually give the necessary density data.
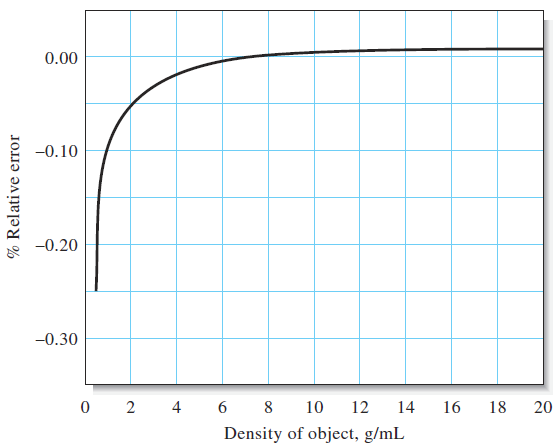
Figure 1.1 Effect of buoyancy on weighing data (density of weights = 8 g/cm3). Plot of relative error as a function of the density of the object weighed.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


