
Coordination number 4
 المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
 المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 543
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 543
 23-2-2017
23-2-2017
 1174
1174
Coordination number 4
4-Coordinate complexes are extremely common, with a tetrahedral arrangement of donor atoms being the most frequently observed. The tetrahedron is sometimes ‘flattened’, distortions being attributed to steric or crystal packing effects or, in some cases, electronic effects. Tetrahedral complexes for d3 ions are not yet known, and for d4 ions have only been stabilized with bulky amido ligands, e.g. [M(NPh2)4] and [M{N(SiMe3)2}3Cl] for M = Hf or Zr. Simple tetrahedral species include:
The solid state structures of apparently simple anions may in fact be polymeric (e.g. the presence of fluoride bridges in [CoF4]2- and [NiF4]2- leads to a polymer with octahedral metal centres) or may be cation-dependent (e.g. discrete tetrahedral [MnCl4]2- ions are present in the Cs and [Me4N]+ salts, but a polymeric structure with Mn_Cl_Mn bridges is adopted by the Na salt). Square planar complexes are rarer than tetrahedral, and are often associated with d8 configurations where electronic factors strongly favour a square planar arrangement (see Section 20.3), e.g. [PdCl4]2-, [PtCl4]2-, [AuCl4]-, [AuBr4]-, [RhCl(PPh3)3] and trans-[IrCl(CO)(PPh))2]. The classification of distorted structures such as those in [Ir(PMePh2)4]+ and [Rh)PMe2Ph(4]+ (Figure 1.1a) may be ambiguous, but in this case, the fact that each metal ion is d8 suggests that steric crowding causes deviation from a square planar arrangement (not from a tetrahedral one). The [Co(CN)4]2- ion is a rare example of a square planar d7 complex.
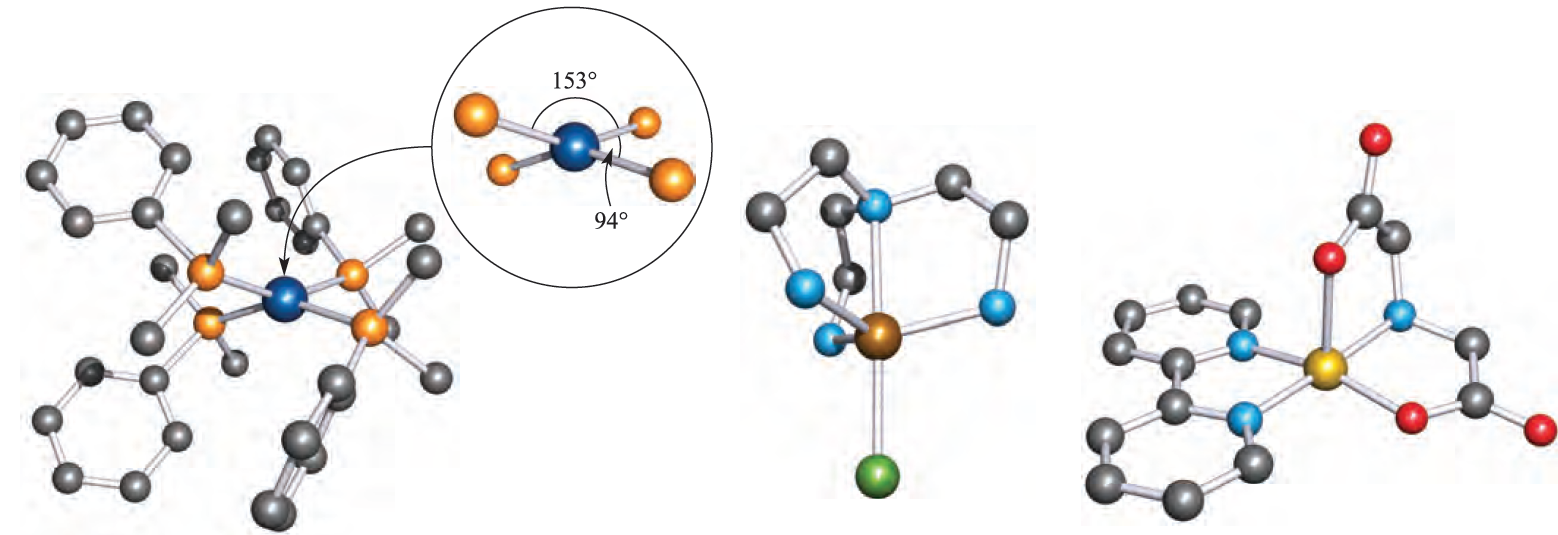
Fig. 1.1 Examples of 4- and 5-coordinate structures (X-ray diffraction data): (a) in [Rh(PMe2Ph)4]+, the steric demands of the ligands distort the structure from the square planar structure expected for this d 8 metal centre [J.H. Reibenspies et al. (1993) Acta Crystallogr., Sect. C, vol. 49, p. 141], (b) [Zn{N(CH2CH2NH2)3}Cl]+ in the [Ph4B]- salt [R.J. Sime et al. (1971) Inorg. Chem., vol. 10, p. 537], and (c) [Cu(bpy){NH(CH2CO2(2}], crystallized as the hexahydrate [R.E. Marsh et al. (1995) Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B, vol. 51, p. 300]. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity; colour code: Rh, dark blue; P, orange; Zn, brown; Cl, green; N, light blue; Cu, yellow; O, red; C, grey.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


