
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
The semiclassical laser equations for the macroscopic quantities electric field strength, polarization and inversion density in the rotating wave- and slowly varying amplitude approximation
المؤلف:
H. HAKEN
المصدر:
LASER LIGHT DYNAMICS
الجزء والصفحة:
vol 2 ، p116
22-12-2016
2044
The semiclassical laser equations for the macroscopic quantities electric field strength, polarization and inversion density in the rotating wave- and slowly varying amplitude approximation
The rotating wave approximation and the slowly varying amplitude approximation cannot only be applied to the laser equations in a resonator, but they may also serve to simplify the laser equations. Since we shall need the thus resulting equations much later in this book, the reader may skip this section and read it only later when it will be needed. We start with the field. With respect to its 1.h.s. we have several options depending on the specific problem, i.e. standing or running waves. When we use standing waves, we are essentially dealing with the field in a resonator. Since this problem, we shall deal here with running waves. Incidentally, this allows us to treat the functional dependence of E on x and t in a symmetric fashion. To this end we consider a plane wave exp[i(kx- i⍵t)] which is slowly modulated in time and space. We therefore write
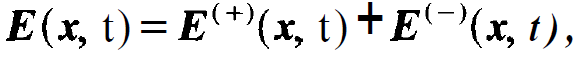 (1 .1)
(1 .1)
where
 (1.2)
(1.2)
and
 (1.3)
(1.3)
We form
 (1.4)
(1.4)
and insert (1.2) in (1.4). This yields
 (1.5)
(1.5)
In the square brackets, the first and fourth term cancel each other, while the third and sixth term can be neglected due to the slowly varying amplitude approximation. In this way (1.4) reduces to
 (1.6)
(1.6)
In a similar, though simpler fashion, we reduce
 (1.7)
(1.7)
to
 (1.8)
(1.8)
In order to transform the r.h.s. we assume P(±) (x, t) in the same form as E(±)(x , t), i.e.
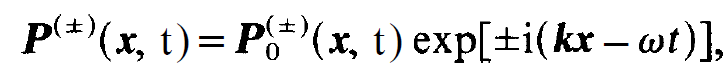 (1.9)
(1.9)
where P0(±) is a function which varies much more slowly in space and time than exp[±i(kx - ⍵t)]. Applying the slowly varying amplitude approximation to μ0 P(±) (x, t), we readily obtain
 (1.10)
(1.10)
We now split the r.h.s. and the 1.h.s. their positive and negative frequency parts, respectively, and collect the corresponding terms (1.6), (1.8) and (1.10). After dividing the resulting equation by exp[i(kx - ⍵t)] we obtain
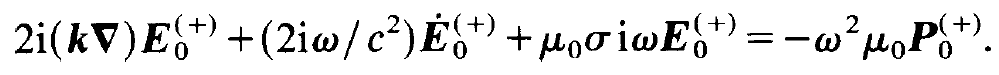 (1.11)
(1.11)
In the last step of our analysis, we multiply this equation by c2/(2iw), use the relations
 (1.12)
(1.12)
and on the r.h.s. of (1.11) the approximation ⍵≈  . This leaves us with the final result, namely the field equation for the slowly varying amplitude
. This leaves us with the final result, namely the field equation for the slowly varying amplitude
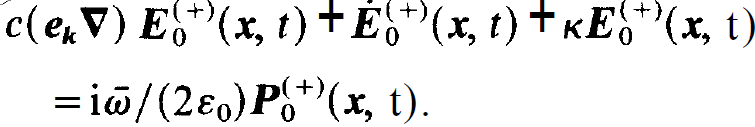 (1.13)
(1.13)
We immediately obtain the equation for the slowly varying amplitude of the polarization
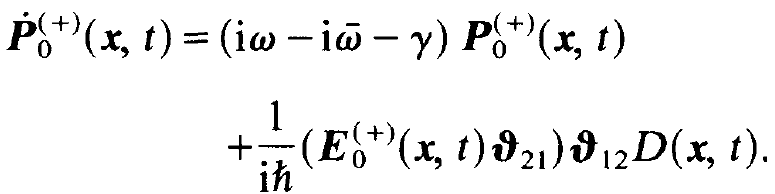 (1.14)
(1.14)
Note that  need not coincide with ⍵, but that we require only |
need not coincide with ⍵, but that we require only | - ⍵|< <⍵,
- ⍵|< <⍵,  . We insert (1.1), (1.2) and (1.10). When we neglect in
. We insert (1.1), (1.2) and (1.10). When we neglect in
 (1.15)
(1.15)
the rapidly oscillating terms  exp[±i(⍵ +
exp[±i(⍵ + )t] we can into the equation for the inversion density containing only slowly varying amplitudes
)t] we can into the equation for the inversion density containing only slowly varying amplitudes
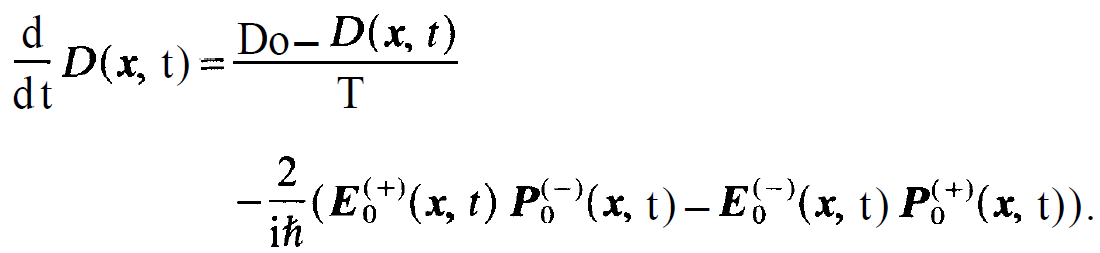 (1.16)
(1.16)
The equations (1.3), (1.4) and (1.16) represent our final result.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الليزر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















