
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Physics without Equations
المؤلف:
Franklin Potter and Christopher Jargodzki
المصدر:
Mad about Modern Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
p 103
6-11-2016
595
Physics without Equations
John von Neumann and Stanislaw Ulam in the 1940s were among the first to consider attempting to
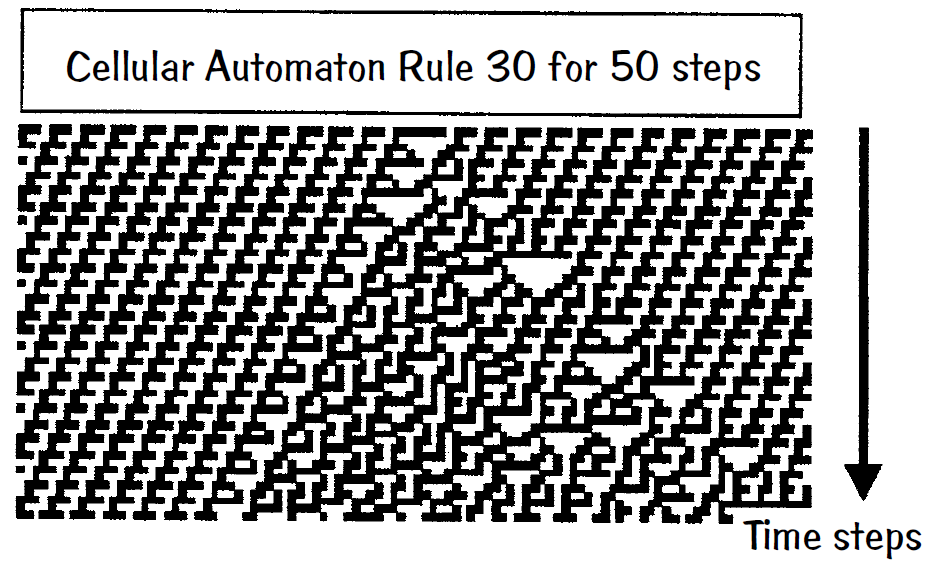
understand natural phenomena via cellular automata and computers. Cellular automata (CA) involve adjacent cells in a 1-D, 2-D, 3-D, and so on grid of cells (or nodes) that take on new numerical values at each tick of the clock according to given rules. The future state of each cell is determined only by the present state of its local neighborhood. One can even remove the external clock and still maintain a progression of states within the CA grid to simulate the passage of time.
Some people claim that all of nature will be simulated eventually on computers using cellular automata. Certainly, fluid flows and other large-scale systems in nature can be simulated to a reasonable degree by CA. But concerning the motion of electrons and other fundamental particles, which involves quantum mechanics and the fundamental interactions, how will these particles show their behavior with this CA technique?
Answer
The best way to use cellular automata (CA) on computers is to incorporate the fundamental interactions of the Standard Model of Leptons and Quarks plus the gravitational interaction of the general theory of relativity, or preferably its quantum gravitational version when available. We know that all these fundamental interactions in nature correspond mathematically to local phase changes, a process that can be simulated with CA without using equations by using a clever enactment of the path-integral approach to doing all of physics in real time. Not yet fully achieved except by very crude approximation, the physics of many-particle interactions will be accomplished by large-scale grid computation methods or perhaps by the equivalent on a quantum computer.
The fundamental idea is to determine the present behavior of a particle by summing over all the phase information from its local environment. Of course, each particle also provides phase information to its environment both near and far. The particle’s new location is the region where the phases match best. The calculation game requires a dynamic limit to how many nearby cells are counted in order to accumulate a good approximation of the phase information and to maintain the local geometrical symmetry. A proof-of-concept calculation has been done by one of us (F. P.) on a desktop computer using thousands of nodes in a 3-D array, but a good calculation requires millions of cells or the equivalent.
The marriage between physics and mathematics has been a happy and fruitful one over many centuries. Mathematical equations, from simple algebraic ones to the more challenging differential equations, have allowed us to summarize an enormous amount of physical phenomena into a simple format. The underlying fundamental symmetries of nature have been the true source of many of these equations. However, formulating these symmetries as the Schrodinger equation and Maxwell’s equations, for example, and solving the equations are human processes. We cannot expect Nature to do the same when the simpler process of looking locally for information is more direct. Therefore we think that understanding the universe by combining CA with path integrals will be the physics of future generations.
 الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
الاكثر قراءة في طرائف الفيزياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















