

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Glutamic Acid
المؤلف:
T. E. Creighton
المصدر:
Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties
الجزء والصفحة:
15-5-2016
2934
Glutamic Acid (Glu, E(
The amino acid glutamic acid is incorporated into the nascent polypeptide chain during protein biosynthesis in response to two codons—GAA and GAG—and represents approximately 6.2% of the residues of the proteins that have been characterized. The glutamyl residue incorporated has a mass of 129.12 Da, a van der Waals volume of 109 Å3, and an accessible surface area of 183 Å2. Glu residues are frequently changed during divergent evolution; they are interchanged in homologous proteins most frequently with aspartic acid, glutamine, alanine, and histidine residues.
The side chain of Glu residues is dominated by its carboxyl group:
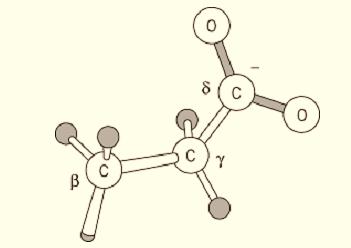
This carboxyl group is normally no more reactive than are those of corresponding organic molecules, such as acetic acid. Its intrinsic pKa value is approximately 4.3, so Glu residues are ionized and very polar under physiological conditions; consequently, very few Glu residues are buried in folded protein structures, and nearly all have at least the carboxyl group on the surface. The pKa can be shifted in folded proteins, however, and either the ionized or nonionized form can be used in the protein's function. For example, carboxyl proteinases have one active-site carboxyl group function in the ionized form, another nonionized. Asp carboxyl groups have a weak intrinsic affinity for Ca2+ ions and are used in many calcium-binding proteins. Certain Glu residues, particularly in proteins involved in blood clotting and bone structure, are carboxylated to yield the unusual residue g-carboxylglutamic acid; such residues have two adjacent carboxyl groups and bind Ca2+ more avidly.
Glu residues differ from Asp only in having two methylene groups, rather than one, so it might be thought that they would be very similar chemically and functionally in proteins, but this is not so. The slight difference in length of the side chains causes them to have different tendencies in their chemical interactions with the peptide backbone, so they have markedly different effects on the conformation and chemical reactivity of the peptide backbone. For example, Glu residues favor the a-helical conformation much more than do Asp. In folded proteins, Glu residues are most frequently found in a-helices, whereas Asp residues occur most frequently in reverse turns .
References
T. E. Creighton (1993) Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties, 2nd ed., W. H. Freeman, New York.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















