

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Electrospray Ionization
المؤلف:
P. Kebarle and L. Tång
المصدر:
Anal. Chem. 65, A972–A986
الجزء والصفحة:
2-5-2016
3011
Electrospray Ionization
Electrospray ionization (ESI) is a method of generating ionic forms of molecules for mass spectrometry . It generates ions directly from solution (usually an aqueous or aqueous/organic solvent system) by creating a fine spray of highly charged droplets in the presence of a strong electric field (1), as shown in Fig. 1. Subsequent vaporization of these charged droplets results in the production of multiply charged gaseous ions. The number of charges retained by an analyte can depend on such factors as the composition and pH of the electrosprayed solvent, as well as the chemical nature of the sample (2-4). For large molecules, the ESI process typically gives rise to a series of multiply charged species for a given analyte. Because mass spectrometers measure the mass-to-charge (m/z) ratio, the resultant ESI mass spectrum contains multiple peaks corresponding to the different charged states (Fig. 2).
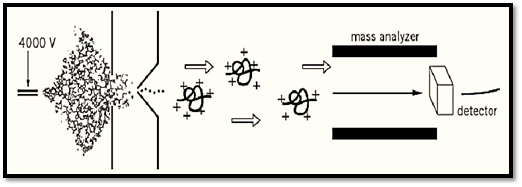
Figure 1. The electrospray ionization process.
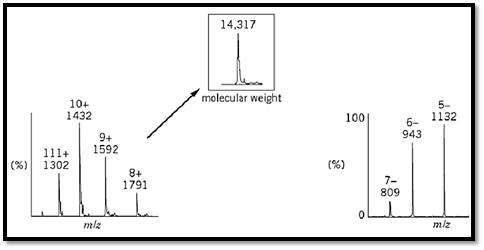
Figure 2. Examples of data generated on an ESI mass spectrometer. Proteins (left) typically produce positive multiply charge generates negative multiply charged ions. The insets for each part show the molecular-weight spectra computer-generated.
The extent of multiple charging that occurs in ESI is a unique characteristic of the technique that enables an analyte's mass to be determined with great precision, as masses can be independently calculated from several different charged states (5). The multiple charging in ESI also permits the analysis of high-molecular-weight analytes, using conventional mass analyzers that are normally limited to the detection of ions with relatively low m/ z ratios. For example, a 50-kDa protein will typically retain on the order of 30 to 50 charges in ESI, yielding multiply charged species with m/z ratios between 1000 and 2000 that are easily detected with quadrupole mass analyzers . Another advantage of ESI-MS is its compatibility as an interface with liquid chromatography. Electrospray ionization is compared to the other common method of ionization in Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization.
References
1. P. Kebarle and L. Tång (1993) Anal. Chem. 65, A972–A986.
2. R. D. Smith, J. A. Loo, C. G. Edmonds, C. J. Barinaga, and H. R. Udseth (1990) Anal. Chem. 62, 882-899.
3. B. T. Chait and S. B. H. Kent (1992) Science 257, 1885–1894.
4. D. Arnott, J. Shabanowitz, and D. F. Hunt (1993) Clinical Chemistry 39, 2005–10.
5. G. Siuzdak (1996) Mass Spectrometry for Biotechnology, Academic Press, San Diego.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















