

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
DNA Dynamics
المؤلف:
A. H.-J. Wang, Y.-G. Gao, Y.-C. Liaw, and Y.-K. Li
المصدر:
Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
25-4-2016
2530
DNA Dynamics
DNA possesses many properties associated with a linear polymer, including various mechanical ) rigidity) and motional properties. The normal B-DNA is considerably more flexible than both A-DNA and Z-DNA. DNA structure in solution has two classes of motional properties: large-scale and local motions. The large scale tumbling motion of a DNA duplex of the size in the range of 10–100 base pairs has a correlation time of nanoseconds to microseconds. It is related to rigidity of the duplex (of varying composition and sequence) as measured by the persistence length. This global flexibility of DNA can be used to understand the behavior of DNA in solution and in gels. There are also local motions that are important in the biological functions of DNA. The dynamic properties of DNA allow it to stretch, bend, twist, and so on. The binding of many intercalators to DNA requires that adjacent DNA base pairs be separated to 6.8 Å in order to accommodate the aromatic intercalator. This is a large conformational change (including sugar pucker rearrangements), involving many torsion angles. Since the binding of intercalators is a reversible process, DNA must be in constant motions, so that the on-off binding process can happen at any time. Figure 1 shows the high resolution structure of the complex between the anticancer drug daunorubicin and CGCGCG crosslinked by formaldehyde (1). Finally, the motion of DNA or drug–DNA complexes may be analyzed by high resolution X-ray crystallography structure refinement that incorporates refinement of anisotropic temperature factors. This demonstrates that various parts of the complex have different motional properties, as is evident in their thermal ellipsoids.
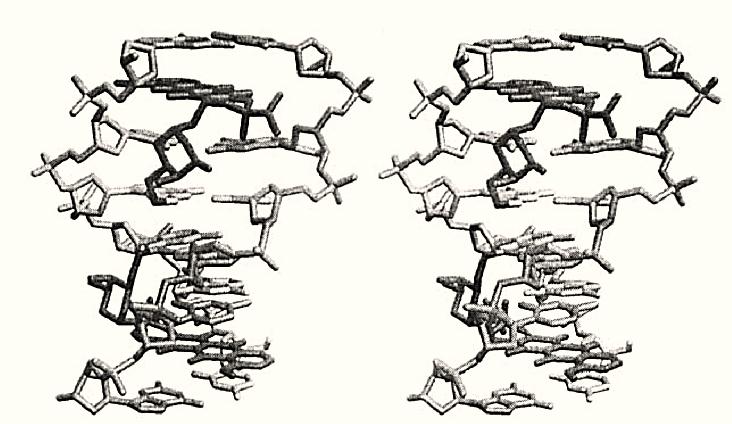
Figure 1. The three-dimensional structure of the daunorubicin–CGCGCG complex (Protein Database DDF023).
Some dinucleotide steps, such as CpG, TpA, or TpG (= CpA), appear to be more flexible (see Base Pairs). In fact, those steps are the preferred binding sites for intercalator binding. They are also the preferred kinked sites induced by binding of proteins. The local dynamic property associated with the CpG site (and other sites) has been probed by high resolution and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (2). The line shape analysis of the 2H-NMR spectra of the dodecamer CGCGAATTCGCG, with the 2H probe incorporated at different sites of the DNA, suggested that the deoxyribose of the C9 residue has a greater motional amplitude than do the other nucleotides. The atypical motional property of the CpG step has been attributed to be correlated with the cleavage at this site by the restriction enzyme EcoRI. Therefore, the local dynamics of DNA clearly play important roles in DNA bending induced by proteins, in binding of intercalators, in restriction enzyme action, and undoubtedly in other biological functions.
References
1. A. H.-J. Wang, Y.-G. Gao, Y.-C. Liaw, and Y.-K. Li (1991) Biochemistry 30, 3812–3815.
2. B. H. Robinson, C. Mailer, and G. Drobny (1997) Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 26, 629–638.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















