

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Most probable number ( MPN) methods ISO 4831:2006 and ISO 7251:2005 for total coliforms and presumptive E. coli in foods
المؤلف:
SILVA, N.D .; TANIWAKI, M.H. ; JUNQUEIRA, V.C.A.; SILVEIRA, N.F.A. , NASCIMENTO , M.D.D. and GOMES ,R.A.R
المصدر:
MICROBIOLOGICAL EXAMINATION METHODS OF FOOD AND WATE A Laboratory Manual
الجزء والصفحة:
18-3-2016
15385
Most probable number ( MPN) methods ISO 4831:2006 and ISO 7251:2005 for total coliforms and presumptive E. coli in foods
These methods of the International Organization for Standardization are applicable to products intended for human consumption or for the feeding of animals, and to environmental samples in the area of food production and food handling.
1 - Material required for analysis
Preparation of the sample and serial dilutions
• Diluent: Saline Peptone Water (SPW) or Buffered Peptone Water (BPW)
• Dilution tubes containing 9 ml Saline Peptone Water (SPW) or Buffered Peptone Water (BPW)
Total coliforms and presumptive E. coli count
• Lauryl Sulfate Tryptose (LST) Broth tubes (10 ml)
• Brilliant Green Bile (BGB) Broth 2% with Durham tubes
• E. coli (EC) Broth with Durham tubes
• Tryptone (Tryptophane) Broth
• Indole Kovacs Reagent
• Laboratory incubator set to 37 ± 1°C
• Water bath or laboratory incubator set to 44 ± 1°C
• Laboratory incubator set to 30 ± 1°C (optional for total coliforms count only)
2 - Procedure
A general flowchart for the enumeration of total colif-orms and presumptive E. coli in foods using the Most Probable Number (MPN) methods ISO 4831:2006 and ISO 7251:2005 is shown in Figure 1.
a) Preparation of the samples and inoculation:
homogenize m grams of the test sample with 9 m milliliters of Saline Peptone Water (SPW) or Buffered Peptone Water (BPW) (10−1 dilution). If the food is acid check the pH of the 10−1 dilution and adjust to 6.8 if necessary (with sterile NaOH).
Note a.1) ISO 4831:2006 and ISO 7251:2005 do not establish the sample quantity in the analytical unity. A commonly weight used is 25 g of the sample in 225 ml of the diluent.
Prepare subsequent decimal dilutions of the sample. Select three appropriate dilutions and inoculate three 1 ml portions of each dilution onto three tubes with 10 ml of Lauryl Sulfate Tryptose Broth (LST).
Note a.2) For some products and/or each time that results of greater accuracy are required, it may be necessary to inoculate series consisting of more then three tubes (e.g. five tubes).
If the expected count is low, inoculate three 10 ml aliquots of the 10−1 dilution onto three tubes with 10 ml of LST Broth double strength, three 1 ml aliquots of the 10−1 dilution onto three tubes with 10 ml of LST Broth single strength, and three 1 ml aliquots of the 10−2 dilution onto three tubes with 10 ml of LST Broth single strength.
For liquid samples with low count it is possible to start the series without dilution: 3 × 10 ml of sample without dilution onto 3 × 10 ml of LST Broth double strength, 3 × 1 ml of sample without dilution onto 3 × 10 ml of LST Broth single strength and 3 × 10 ml of 10−1 dilution onto 3 × 10 ml of LST Broth single strength. If the food is acid adjust the pH of the three double strength LST tubes to 6.8 after the inoculation (with sterile NaOH).
For liquid samples with low count it is also possible to apply a MPN single dilution test, inoculating 5 × 10 ml aliquots of the sample without dilution onto 5 × 10 ml of LST Broth double strength. If the food is acid adjust the pH of the five double strength LST tubes to 6.8 after the inoculation (with sterile NaOH).
b) Incubation for presumptive test (ISO 4831:2006 and 7251:2005): Incubate LST tubes at 37 ± 1°C/24 ± 2 h. Examine tubes and record reactions at 24 ± 2 h for gas (displacement of medium in fermentation vial or effervescence when tubes are
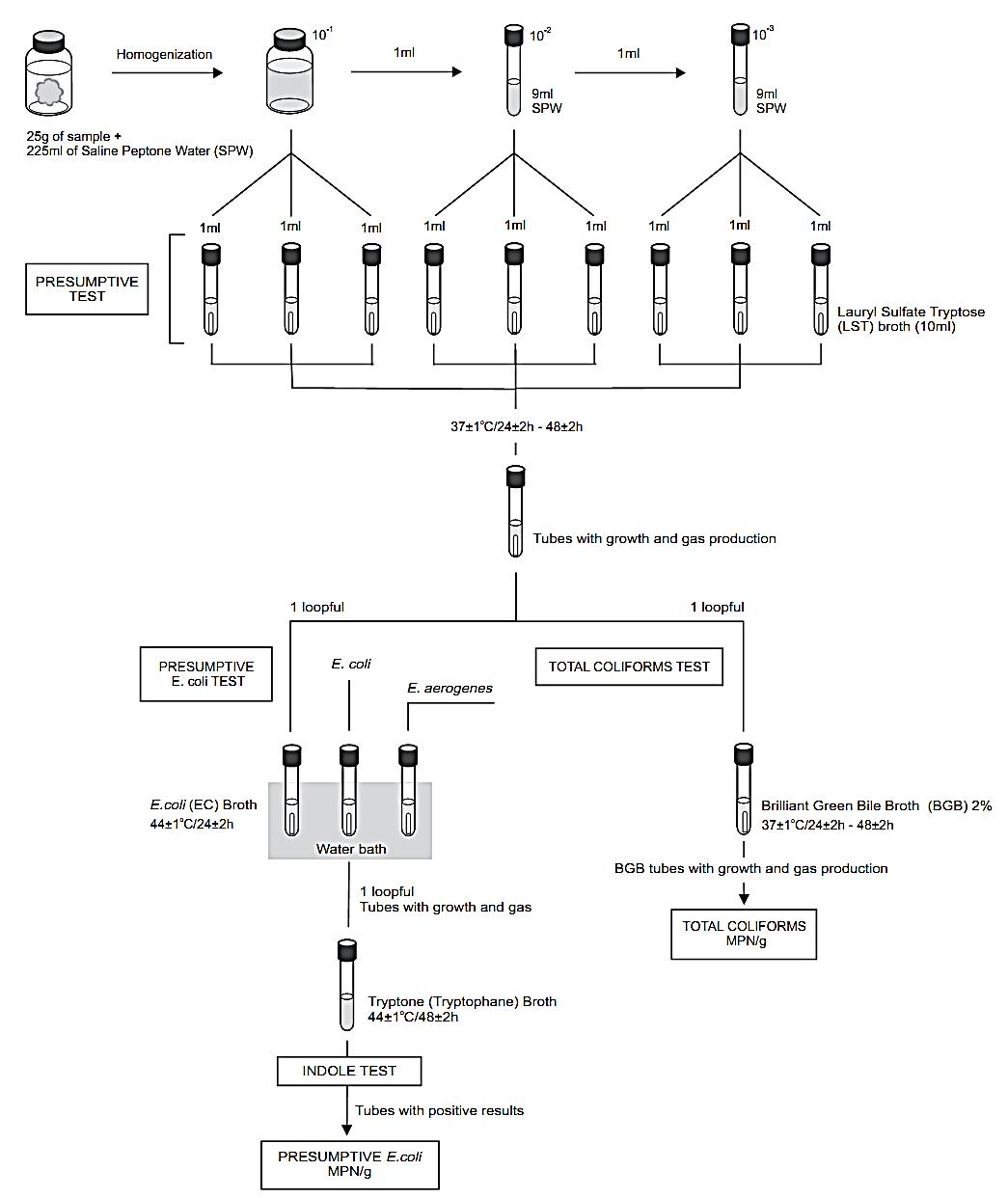
Figure 1 Scheme of analysis for the enumeration of total coliforms and presumptive E. coli in foods using the Most Probable Number (MPN) methods ISO 4831:2006 and ISO 7251:2005.
gently agitated). Re-incubate gas-negative tubes for an additional 24 h and examine and record reactions again at 48 ± 2 h. Perform confirmed test on all presumptive positive (gas) tubes.
Note b.1) When performing only the total coliform count (ISO 4831:2006) it is possible to choose between two incubation temperatures, 30 ± 1°C or 37 ± 1°C (30 ± 1°C is indicated for milk and milk products). The temperature is subject of agreement between parties concerned. The incubation time for double strength LST tubes is 24 ± 2 h without re-incubation of negative tubes. For single strength LST tubes the negative tubes are re-incubated for an additional 24 ± 2 h.
c) Confirmed test for total coliforms (ISO 4831:2006): From each double strength LST tube showing gas after 24 ± 2 h of incubation, transfer a loopful of the suspension to a tube of Brilliant Green Bile Broth (BGB).
From each single strength LST tube showing gas after 24 ± 2 h or 48 ± 2 h of incubation, transfer a loopful of the suspension to a tube of Brilliant Green Bile Broth (BGB).
Incubate the BGB tubes at 37 ± 1°C/24 ± 2 h and examine for gas production, indicative of a positive result. Re-incubate gas-negative tubes for an additional 24 h and examine and record reactions again at 48 ± 2 h. Calculate most probable number (MPN).
Note c.1) If the LST tubes were incubated at 30 ± 1°C in the previous step, use the same temperature to incubate the BGB tubes.
d) Test for presumptive E. coli (ISO 7251:2005) d.1) Test for growth and gas production in EC Broth at 44°C: From each LST tube show-ing gas, transfer a loopful of the suspension to a tube of E. coli Broth (EC). Incubate the EC tubes at 44 ± 1°C/24 ± 2 h (water bath or incubator). Examine the tubes for gas production and re-incubate the gas-negative tubes for an additional 24 h ± 2 h.
Note d.1) For some milk products (e.g. casein), the Durham tube may stick to the bottom of the LST tubes. If, after 48 h incubation period, growth is observed but no gas production, inoculate this LST culture into EC broth.
Note d.2) For double strength LST tubes, the opacity or cloudiness may difficult the gas observation. In this case inoculate this LST culture into EC broth.
Note d.3) For live shellfish, an incubation time of not more than 24 ± 2 h may be used.
d.2) Indole test at 44°C: From each EC tube showing gas (in 24 or 48 h of incubation) inoculate a tube of Tryptone (Tryptophane) Broth. Incubate the tubes at 44 ± 1°C/48 ± 2 h and test for indole production: Add 0.5 ml of the Indole Kovacs Reagent to each tube of Tryptone (Tryptophane) Broth, mix well and examine after 1 min. A red color in the alcoholic phase (surface of the liquid) indicates indole production.
Consider as presumptive E. coli the cultures showing gas in EC Broth at 44°C and indole production in Tryptone (Tryptophane) Broth at 44°C. Calculate most probable number (MPN) .
References
Silva, N.D .; Taniwaki, M.H. ; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Silveira, N.F.A. , Nasdcimento , M.D.D. and Gomes ,R.A.R .(2013) . Microbiological examination methods of food and water a laboratory Manual. Institute of Food Technology – ITAL, Campinas, SP, Brazil .
International Organization for Standardization (2005) ISO 7251:2005. Microbiology of food and animal stuffs – Horizontal method for the detection and enumeration of presumptive Escherichia coli – Most probable number technique. Geneva, ISO.
International Organization for Standardization (2006) ISO 4831:2006. Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs – Horizontal method for the detection and enumeration of coliforms – Most probable number technique. Geneva, ISO.
 الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















