
PRIONS
 المؤلف:
Carroll, K. C., Hobden, J. A., Miller, S., Morse, S. A., Mietzner, T. A., Detrick, B
المؤلف:
Carroll, K. C., Hobden, J. A., Miller, S., Morse, S. A., Mietzner, T. A., Detrick, B
 المصدر:
Jawetz, Melnick, & Adelberg’s Medical Microbiology
المصدر:
Jawetz, Melnick, & Adelberg’s Medical Microbiology
 الجزء والصفحة:
27E , P3
الجزء والصفحة:
27E , P3
 2024-12-22
2024-12-22
 1189
1189
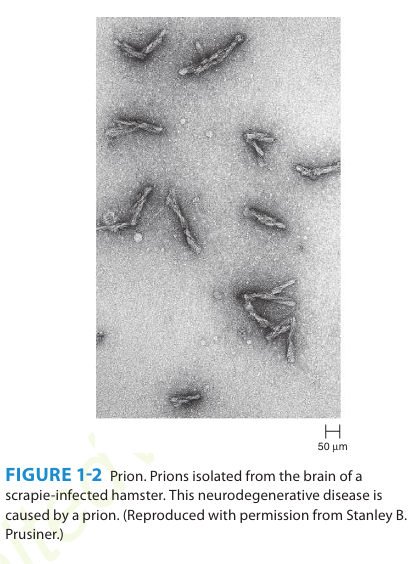
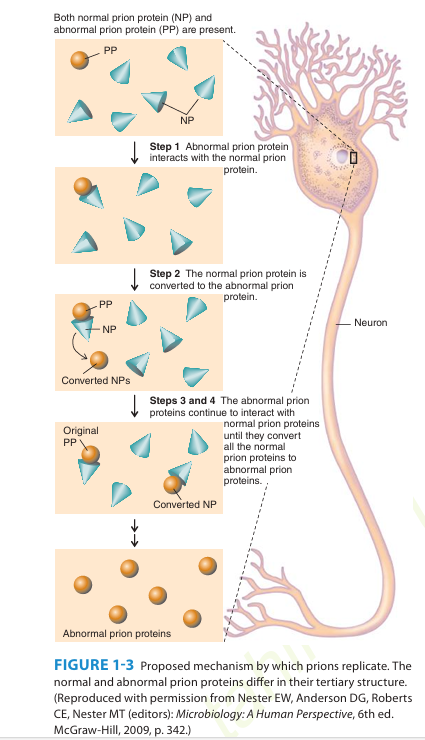
A number of remarkable discoveries in the past three decades have led to the molecular and genetic characterization of the transmissible agent causing scrapie, a degenerative central nervous system disease of sheep. Studies have identified a scrapie-specific protein in preparations from scrapie-infected brains of sheep that is capable of reproducing the symptoms of scrapie in previously uninfected sheep. Attempts to identify additional components, such as nucleic acid, have been unsuccessful. To distinguish this agent from viruses and viroids, the term prion was introduced to emphasize its proteinaceous and infectious nature. The cellular form of the prion protein (PrPc) is encoded by the host's chromosomal DNA. PrP is a sialoglycoprotein with a molecular mass of 33,000-35,000 Da and a high content of α-helical secondary structure that is sensitive to proteases and soluble in detergent. PrPc is expressed on the surface of neurons via a glycosylphosphatidyl inositol anchor in both infected and uninfected brains. A conformational change occurs in the prion protein, changing it from its normal or cellular form PrPc to the disease-causing conformation, Prpsc. When Prpsc is present in an individual (owing to spontaneous conformational conversion or to infection), it is capable of recruiting PrPc and converting it to the disease form. Thus, prions replicate using the PrPc substrate that is present in the host.
There are additional prion diseases of importance. Kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease, and fatal familial insomnia affect humans. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy, which is thought to result from the ingestion of feeds and bone meal prepared from rendered sheep offal, has been responsible for the deaths of more than 184,000 cattle in Great Britain since its discovery in 1985. A new variant of CJD (vCJD) has been associated with human ingestion of prion-infected beef in the United Kingdom and France. A common feature of all of these diseases is the conversion of a host-encoded sialoglycoprotein to a protease-resistant form as a consequence of infection.
Human prion diseases are unique in that they manifest as sporadic, genetic, and infectious diseases. The study of prion biology is an important emerging area of biomedical investigation, and much remains to be learned.
 الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


