

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Substitution
المؤلف:
Jim Miller
المصدر:
An Introduction to English Syntax
الجزء والصفحة:
15-2
28-1-2022
1636
Substitution
The essential idea behind this test is that a single word can substitute for a number of words hanging together as a phrase. This is demonstrated in (9)
 Them in (9b) substitutes for the intriguing results of the latest examination in (9a). Similarly, in (6a) and (6b) David can be substituted for the pupils in this maths class: David baked cakes for Margaret every Friday and Cakes were baked for Margaret every Friday by David.
Them in (9b) substitutes for the intriguing results of the latest examination in (9a). Similarly, in (6a) and (6b) David can be substituted for the pupils in this maths class: David baked cakes for Margaret every Friday and Cakes were baked for Margaret every Friday by David.
The test of substitution applies to sequences of words with adjectives, such as those in (7); This parcel is very heavy, This parcel is astonishingly and frighteningly heavy or simply This parcel is heavy. The single adjective heavy substitutes for the sequences very heavy and astonishingly and frighteningly heavy but another type of substitution is possible, using the specialized substitution word so. Consider the dialogue in (10). (Here capital letters represent different speakers.)
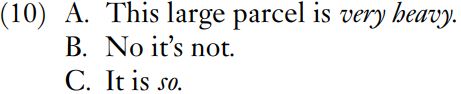
The test of so-substitution exemplified in (10) is straightforward in that the sequence very heavy is removed and so is dropped into the empty slot. Another type of so-substitution is rather indirect. Consider (11).
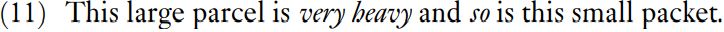
There is no doubt that so ‘stands for’ very heavy. The reason for calling
this substitution ‘indirect’ is that so has not simply been dropped into the slot occupied by very heavy but has been moved to the front of the clause. Nonetheless, so-substitution is a good indication that sequences such as very heavy form a larger unit.
Substitution can be applied to sequences introduced by prepositions, as in (12) and (13).

There in (12b) substitutes for in the lounge in (12a), and here in (13b) substitutes for to Mr Chalky’s school in (13a). Examples in which a single preposition substitutes for a whole sequence are difficult to find. This is mainly because prepositions typically require a complement, but also because in standard written English there is a contrast between in for location and into for movement, and for many speakers there is a contrast between out of for movement and out for location, as in (14).

In informal spoken English, and certainly in non-standard varieties of English, in and out express both location and movement, and (14b, c) can be expressed as (15a, b).
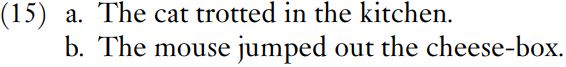
These examples can be shortened to those in (16).
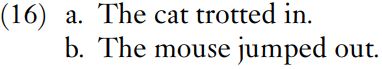
In these examples, in and out can be treated as single words substituting for the longer phrases in the kitchen and out the cheese-box. However, for the large majority of prepositions, the substitution of a preposition for preposition plus noun phrase does not work, whether in writing or informal speech, in standard or non-standard English.
Finally in this section, let us note that all the above examples show a sequence of words being replaced by one word. The converse is that a single word can be replaced by a sequence of words: Cheese is good can be changed to That French cheese with the blue veins is good. The latter example is occasionally described in terms of cheese being expanded to that French cheese with the blue veins, but it is treated here as a type of substitution.
 الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















