

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Hydrogenation with Heterogeneous Catalysts
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
الجزء والصفحة:
........
21-1-2022
3877
Hydrogenation with Heterogeneous Catalysts
Addition of hydrogen to a multiple bond is hydrogenation. It is applicable to almost all types of multiple bonds and is of great importance in synthetic chemistry, particularly in the chemical industry. Probably the most important technical example is production of ammonia by the hydrogenation of nitrogen:
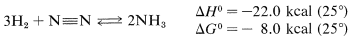
This may appear to be a simple process, but in fact it is difficult to carry out because the equilibrium is not very favorable. High pressures (150-200 atm) are required to get a reasonable conversion, and high temperatures (430-510o) are necessary to get reasonable reaction rates. A catalyst, usually iron oxide, also is required. The reaction is very important because ammonia is used in ever-increasing amounts as a fertilizer either directly or through conversion to urea or ammonium salts.
Production of ammonia requires large quantities of hydrogen, most of which comes from the partial oxidation of hydrocarbons with water or oxygen. A simple and important example is the so-called "methane-steam gas" reaction, which is favorable only at very high temperatures because of the entropy effect in the formation of H2 :
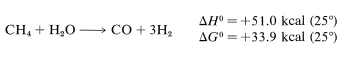
Therefore the fertilizer industry is allied closely with the natural gas and petroleum industries, and for obvious reasons ammonia and hydrogen often are produced at the same locations.,
Alkenes and alkynes add hydrogen much more readily than does nitrogen. For example, ethene reacts rapidly and completely with hydrogen at ordinary pressures and temperatures in the presence of metal catalysts such as nickel, platinum, palladium, copper, and chromium:
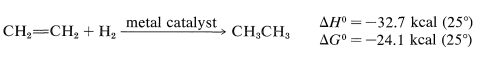
These reactions are unlike any we have encountered so far. They are heterogeneous reactions, which means that the reacting system consists of two or more phases. Usually, the metal catalyst is present as a finely divided solid suspension in the liquid or solution to be reduced. Alternatively, the metal is deposited on an inert solid support such as carbon, barium sulfate, alumina (Al2O3), or calcium carbonate. Then the mixture of the liquid substrate and solid catalyst is shaken or stirred in a hydrogen atmosphere. However, then actual reaction takes place at the surface of the metal catalyst and is an example of heterogeneous or surface catalysis.
 الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















