

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Steps in Translation : Translation regulation ,Protein folding and Protein targeting
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
28-12-2021
1760
Steps in Translation : Translation regulation ,Protein folding and Protein targeting
Translation regulation
Gene expression is most commonly regulated at the transcriptional level, but translation may also be regulated. An important mechanism by whichthis is achieved in eukaryotes is by covalent modification of eIF-2: Phosphorylated eIF-2 is inactive . In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, regulation can also be achieved through proteins that bind mRNA and inhibit its use by blocking translation.
E. Protein folding
Proteins must fold to assume their functional, native state. Folding can be spontaneous (as a result of the primary structure) or facilitated by proteins known as chaperones .
F. Protein targeting
Although most protein synthesis in eukaryotes is initiated in the cytoplasm, many proteins perform their functions within subcellular organelles or outside of the cell. Such proteins normally contain amino acid sequences that direct the proteins to their final locations. For example, secreted proteins are targeted during synthesis (cotranslational targeting) to the RER by the presence of an N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence. The sequence is recognized by the signal recognition particle (SRP), a
ribonucleoprotein that binds the ribosome, halts elongation, and delivers the ribosome–peptide complex to an RER membrane channel (the translocon) via interaction with the SRP receptor. Translation resumes, the protein enters the RER lumen, and its signal sequence is cleaved (Fig. 1). The protein moves through the RER and the Golgi, is processed, packaged into vesicles, and secreted. Proteins targeted after synthesis (posttranslational) include nuclear proteins that contain an internal, short, basic nuclear localization signal; mitochondrial matrix proteins that contain an Nterminal, amphipathic, α-helical mitochondrial entry sequence; and peroxisomal proteins that contain a C-terminal tripeptide signal.
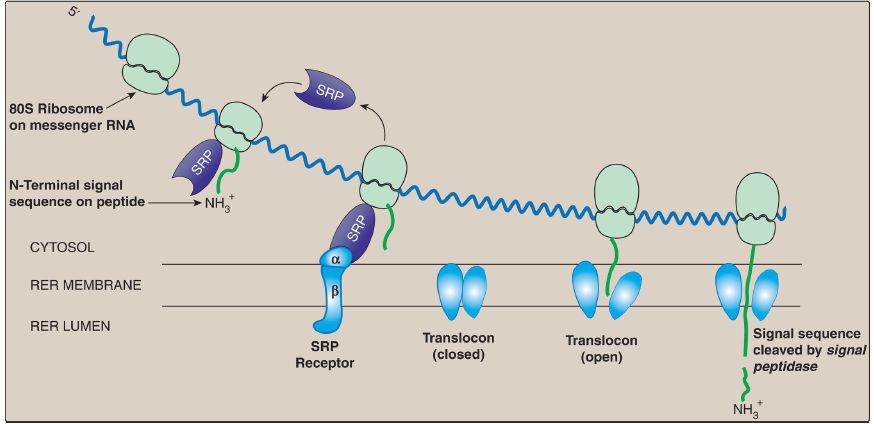
Figure 1: Cotranslational targeting of proteins to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). SRP = signal recognition particle.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















