

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Macrominerals : Sodium, chloride, and potassium
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
16-12-2021
1519
Macrominerals : Sodium, chloride, and potassium
These macrominerals are considered together because they play important roles in several physiologic processes. For example, they maintain water balance, osmotic equilibrium, acid–base balance (pH), and the electrical gradients across cell membranes (membrane potential) that are essential for the functioning of neurons and myocytes.
1. Sodium and chloride: Na+ and Cl− are primarily extracellular electrolytes. They are readily absorbed from foods containing salt (NaCl), much of which comes from processed foods. [Note: Na+ is required for the intestinal absorption (and renal reabsorption) of glucose and galactose and free amino acids by Na+-linked transporters. Cl− is used to form hydrochloric acid required for digestion .] In the United States, the average daily consumption of NaCl is 1.5–3 times the adequate intake (AI) of 3.8 mg/day (UL = 5.8 g/day). Dietary deficiency is rare.
a. Hypertension: Na+ intake is related to blood pressure (BP). Ingestion of Na+ stimulates thirst centers in the brain and secretion of antidiuretic hormone from the pituitary, leading to water retention. This results in an increase in plasma volume and, consequently, an increase in BP.
Chronic hypertension can damage the heart, kidneys, and blood vessels. Modest reductions in Na+ intake have been shown to result in modest reductions in BP. [Note: Some populations (for example, African Americans) are “salt sensitive” and have larger responses to Na+.]
b. Hyper- and hyponatremia: Hypernatremia, typically caused by excess water loss, and hyponatremia, typically caused by decreased ability to excrete water, can result in severe brain damage. [Note: Chronic hyponatremia increases Ca2+ excretion and can result in osteoporosis (low bone mass).]
2. Potassium: In contrast to Na+, K+ is primarily an intracellular electrolyte. [Note: The concentration differential of Na+ and K+ across the cell membrane is maintained by the Na+/K+ ATPase (Fig. 29.4).] In contrast to Na+ and Cl−, K+ (like Mg2+) is underingested in Western diets because its primary sources, fruits and vegetables, are underingested. [Note: Increasing dietary K+ decreases BP by increasing Na+ excretion.] There is a narrow range for normal serum K+ levels, and even modest changes (up or down, resulting in hyper- or hypokalemia) can result in cardiac arrhythmias and skeletal muscle weakness. [Note: Hypokalemia can result from the inappropriate use of laxatives to lose weight.] No UL for K+ has been established.
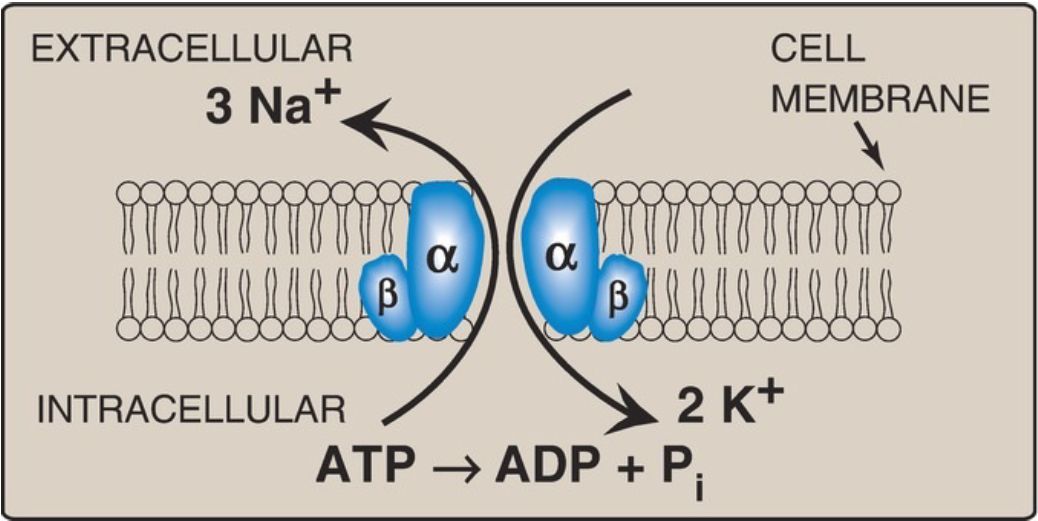
Figure 1: Na+/K+ ATPase. Na+ = sodium; K+ = potassium; ADP = adenosine diphosphate; Pi = phosphate.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















