
Glycosphingolipid Synthesis and Degradation
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 16-10-2021
16-10-2021
 2369
2369
Glycosphingolipid Synthesis and Degradation
Synthesis of glycosphingolipids occurs primarily in the Golgi by sequential addition of glycosyl monomers transferred from UDP-sugar donors to the acceptor molecule. The mechanism is similar to that used in glycoprotein synthesis.
A. Enzymes involved in synthesis
The enzymes involved in the synthesis of glycosphingolipids are glycosyltransferases that are specific for the type and location of the glycosidic bond formed. [Note: These enzymes can recognize both glycosphingolipids and glycoproteins as substrates.]
B. Sulfate group addition
A sulfate group from the sulfate carrier 3ʹ-phosphoadenosine-5ʹ-phosphosulfate ([PAPS], Fig. 1) is added by a sulfotransferase to the 3ʹ-hydroxyl group of the galactose in a galactocerebroside, forming the sulfatide galactocerebroside 3-sulfate (Fig. 2). [Note: PAPS is also the sulfur donor in glycosaminoglycan synthesis (see p. 162) and steroid hormone catabolism .] An overview of the synthesis of sphingolipids is shown in Figure 3.
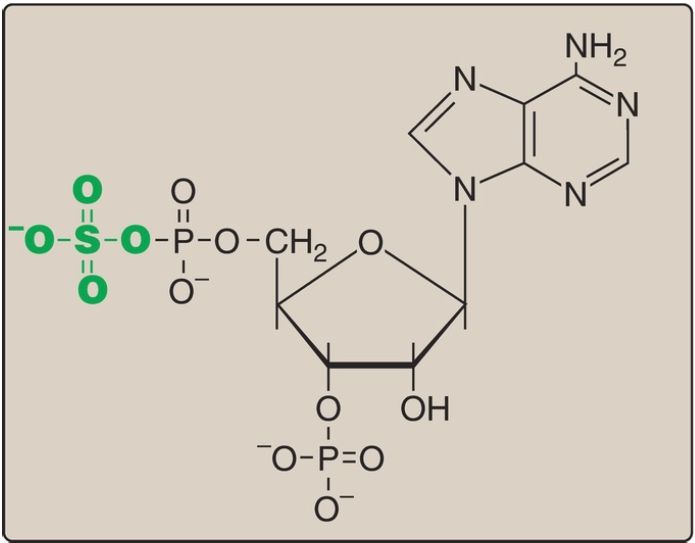
Figure 1: Structure of 3′-phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphosulfate.
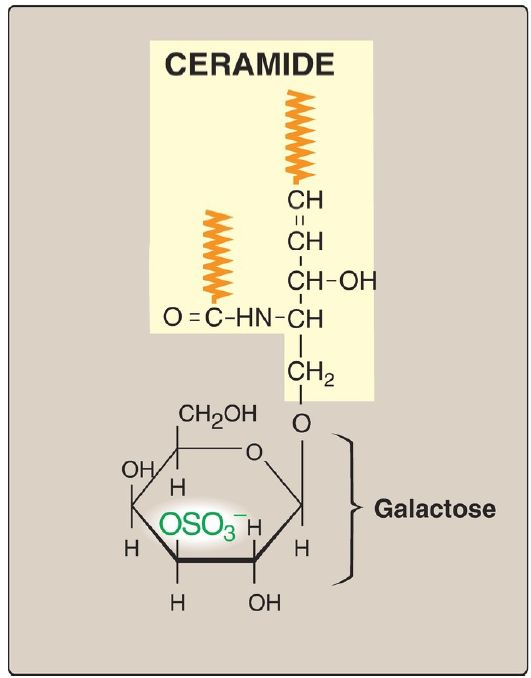
Figure 2: Structure of galactocerebroside 3-sulfate. ( is a hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain.)
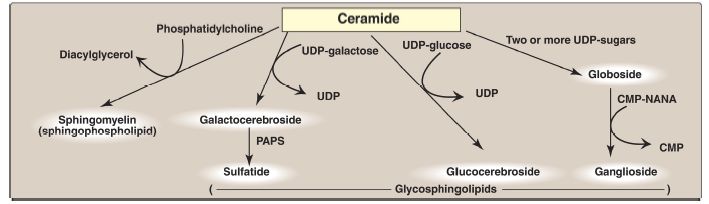
Figure 3: Overview of sphingolipid synthesis. UDP = uridine diphosphate; CMP = cytidine monophosphate; NANA = N-acetylneuraminic acid; PAPS = 3ʹ- phosphoadenosine-5ʹ-phosphosulfate.
C. Glycosphingolipid degradation
Glycosphingolipids are internalized by phagocytosis as described for the glycosaminoglycans . All of the enzymes required for the degradative process are present in lysosomes, which fuse with the phagosomes. The lysosomal enzymes hydrolytically and irreversibly cleave specific bonds in the glycosphingolipid. As seen with the glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins , degradation is a sequential process following the rule “last on, first off,” in which the last group added during synthesis is the first group removed in degradation. Therefore, defects in the degradation of the polysaccharide chains in these three glycoconjugates result in lysosomal storage diseases.
D. Sphingolipidoses
In a normal individual, synthesis and degradation of glycosphingolipids are balanced, so that the amount of these compounds present in membranes is constant. If a specific lysosomal acid hydrolase required for degradation is partially or totally missing, a sphingolipid accumulates. Lysosomal lipid storage diseases caused by these deficiencies are called sphingolipidoses. The result of a specific acid hydrolase deficiency may be seen dramatically in nerve tissue, where neurologic deterioration can lead to early death. [Note: Some sphingolipidoses can also result from defects in lysosomal activator proteins (for example, the saposins) that facilitate access of the hydrolases to short carbohydrate chains as degradation proceeds.]
1. Common properties: A specific lysosomal hydrolytic enzyme is deficient in the classic form of each disorder. Therefore, usually, only a single sphingolipid (the substrate for the deficient enzyme) accumulates in the involved organs in each disease. [Note: The rate of biosynthesis of the accumulating lipid is normal.] The disorders are progressive and, although many are fatal in childhood, extensive phenotypic variability is seen leading to the designation of different clinical types, such as types A and B in Niemann-Pick disease. Genetic variability is also seen because a given disorder can be caused by any one of a variety of mutations within a single gene. The sphingolipidoses are autosomal-recessive disorders, except for Fabry disease, which is X linked. The incidence of the sphingolipidoses is low in most populations, except for Gaucher and Tay-Sachs diseases, which, like Niemann-Pick disease, show a high frequency in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. [Note: Tay-Sachs also has a high frequency in Irish American, French Canadian, and Louisiana Cajun populations.]
2. Diagnosis and treatment: A specific sphingolipidosis can be diagnosed by measuring enzyme activity in cultured fibroblasts or peripheral leukocytes or by analyzing DNA. Histologic examination of the affected tissue is also useful. [Note: Shell-like inclusion bodies are seen in Tay-Sachs, and a crumpled tissue paper appearance of the cytosol is seen in Gaucher disease (Fig. 4).] Prenatal diagnosis, using cultured amniocytes or chorionic villi, is available. Gaucher disease, in which macrophages become engorged with glucocerebroside, and Fabry disease, in which globosides accumulate in the vascular endothelial lysosomes of the brain, heart, kidneys, and skin, are treated by recombinant human enzyme replacement therapy, but the monetary cost is extremely high. Gaucher has also been treated by bone marrow transplantation (because macrophages are derived from hematopoietic stem cells) and by substrate reduction therapy through pharmacologic reduction of glucosylceramide, the substrate for the deficient enzyme.
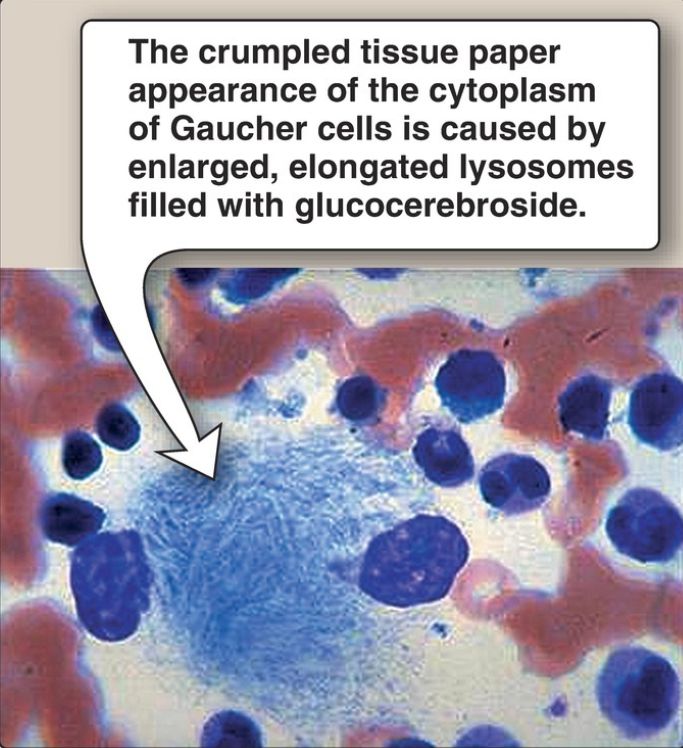
Figure 4: Aspirated bone marrow cells from a patient with Gaucher disease.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


