
Structure of Elastin
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 3-9-2021
3-9-2021
 2541
2541
Structure of Elastin
In contrast to collagen, which forms fibers that are tough and have high tensile strength, elastin is a connective tissue fibrous protein with rubber-like properties.
Elastic fibers composed of elastin and glycoprotein microfibrils are found in the lungs, the walls of large arteries, and elastic ligaments. They can be stretched to several times their normal length but recoil to their original shape when the stretching force is relaxed.
Elastin is an insoluble protein polymer generated from a precursor, tropoelastin, which is a soluble polypeptide composed of ~700 amino acids that are primarily small and nonpolar (for example, glycine, alanine, and valine). Elastin is also rich in proline and lysine but contains scant hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine. Tropoelastin is secreted by the cell into the ECM. There, it interacts with specific glycoprotein microfibrils, such as fibrillin, which function as a scaffold onto which tropoelastin is deposited.
Some of the lysyl side chains of the tropoelastin polypeptides are oxidatively deaminated by lysyl oxidase, forming allysine residues. Three of the allysyl side chains plus one unaltered lysyl side chain from the same or neighboring polypeptides form a desmosine cross-link (Fig. 1). This produces elastin, an extensively interconnected, rubbery network that can stretch and bend in any direction when stressed, giving connective tissue elasticity (Fig. 2). Mutations in the fibrillin-1 protein are responsible for Marfan syndrome, a connective tissue disorder characterized by impaired structural integrity in the skeleton, the eye, and the cardiovascular system.
With this disease, abnormal fibrillin protein is incorporated into microfibrils along with normal fibrillin, inhibiting the formation of functional microfibrils. [Note: Patients with Marfan syndrome, OI, or EDS may have blue sclerae due to tissue thinning that allows underlying pigment to show through.]
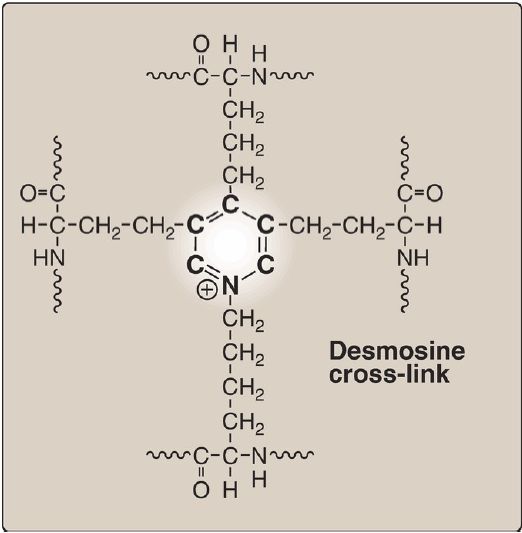
Figure 1: Desmosine cross-link unique to elastin.
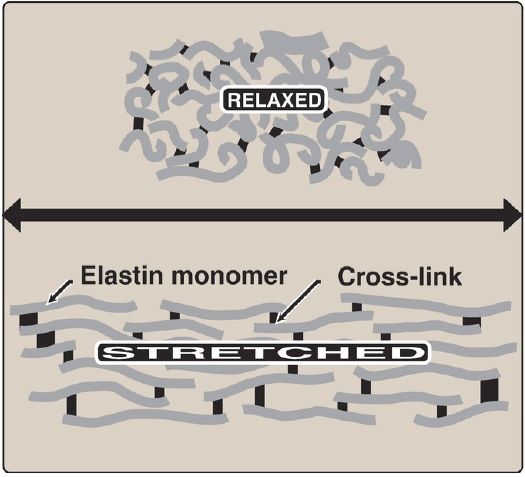
Figure 2: Elastin fibers in relaxed and stretched conformations.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


