

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Collagenopathies
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
3-9-2021
1571
Collagenopathies
Defects in any one of the many steps in collagen fiber synthesis can result in a genetic disease involving an inability of collagen to form fibers properly and, therefore, an inability to provide tissues with the needed tensile strength normally provided by collagen. More than 1,000 mutations have been identified in 23 genes coding for 13 of the collagen types. The following are examples of diseases (collagenopathies) that are the result of defective collagen synthesis.
1. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a heterogeneous group of connective tissue disorders that result from heritable defects in the metabolism of fibrillar collagen molecules. EDS can be caused by a deficiency of collagen-processing enzymes (for example, lysyl hydroxylase or N-procollagen peptidase) or from mutations in the amino acid sequences of collagen types I, III, and V.
The classic form of EDS, caused by defects in type V collagen, is characterized by skin extensibility and fragility and joint hypermobility (Fig. 1). The vascular form, due to defects in type III collagen, is the most serious form of EDS because it is associated with potentially lethal arterial rupture. [Note: The classic and vascular forms show autosomaldominant inheritance.] Collagen that contains mutant chains may have altered structure, secretion, or distribution, and it frequently is degraded. [Note: Incorporation of just one mutant chain may result in degradation of the triple helix. This is known as a dominant-negative effect.]
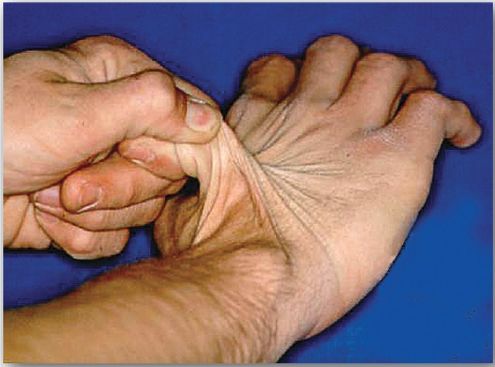
Figure 1 Stretchy skin of classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
2. Osteogenesis imperfecta: This syndrome, known as “brittle bone disease,” is a genetic disorder of bone fragility characterized by bones that fracture easily, with minor or no trauma (Fig. 2). Over 80% of cases of osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) are caused by dominant mutations to the genes that encode the α1 or α2 chains in type I collagen. The most common mutations cause the replacement of glycine (in –Gly–X–Y–) by amino acids with bulky side chains. The resultant structurally abnormal α chains prevent the formation of the required triple-helical conformation.
Phenotypic severity ranges from mild to lethal. Type I OI, the most common form, is characterized by mild bone fragility, hearing loss, and blue sclerae. Type II, the most severe form, is typically lethal in the perinatal period as a result of pulmonary complications. In utero fractures are seen (see Fig. 2). Type III is also a severe form and is characterized by multiple fractures at birth, short stature, spinal curvature leading to a humped-back (kyphotic) appearance, and blue sclerae. Dentinogenesis imperfecta, a disorder of tooth development, may be seen in OI.
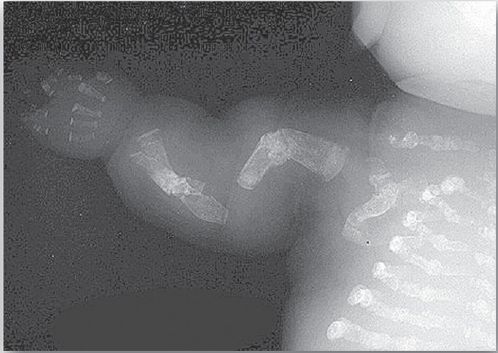
Figure 2: Lethal form (type II) of osteogenesis imperfecta in which the fractures appear in utero, as revealed by this radiograph of a stillborn fetus.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















