
H Chains Are Assembled by Two Sequential Recombination Events
 المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
 المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 29-4-2021
29-4-2021
 2040
2040
H Chains Are Assembled by Two Sequential Recombination Events
KEY CONCEPTS
- The units for H chain recombination are a VH gene, a D segment, and a JH -CH gene segment.
- The first recombination joins D to JH -CH . The second recombination joins VH to DHJH -CH to yield VH -DHJH -CH .
- The CH segment consists of four exons.
The IgH locus includes an additional set of gene segments, the D segments. Thus, the assembly of a complete H chain entails recombination of VH , D, and JH genes. The D segment (for diversity) was discovered by the presence in the H chain peptide sequences of an extra 2 to 13 amino acids between the sequences coded by the VH and the JH segments. An array of D segments lies on the chromosome between the cluster of VH segments and that of JH segments.
VH DJH joining takes place in two stages (FIGURE 1). First, one of the D segments recombines with a JH segment; second, a VH segment recombines with the already recombined DJHsegment. The resulting VH DJH DNA sequence is then expressed with the nearest downstream CH gene, which consists of a cluster of four exons (the use of different CH genes is discussed in the section in this chapter titled Class Switch DNA Recombination). The D segments are organized in a tandem array. The human locus comprises about 30 D segments, followed by a cluster of 6 JH gene segments. The same D segment is involved in the DJH recombination and related VH DJH recombination.
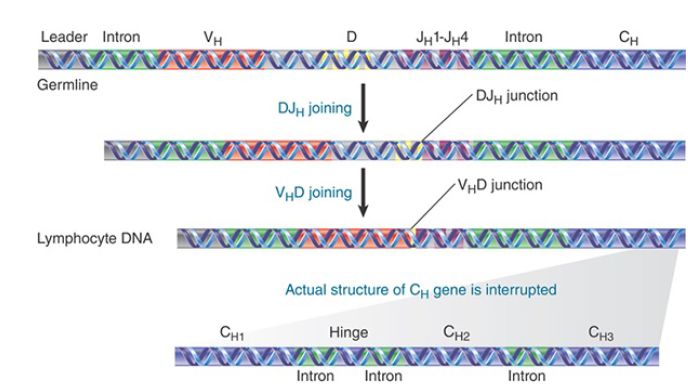
FIGURE 1. Heavy genes are assembled by sequential recombination events. First a DH segment is recombined with a JH segment, and then a VH gene segment is recombined with the DH segment.
The structure of recombined V(D)J segments is similar in organization in the H chain and λ and κ chain loci. The first exon codes for the signal sequence, which is involved in membrane attachment, and the second exon codes for the major part of the variable region itself, which is about 100 codons long. The remainder of the variable region is provided by the D segment (in the H chain locus only) and by a J segment (in all three loci).
The structure of the C region differs in different H and L chains. In both κ and λ chains, the C region is encoded by a single exon, which becomes the third exon of the recombined Vκ Jκ -Cκ or Vλ Jλ - Cλ gene. In H chains, the C region is encoded by multiple and discrete exons, separately coding for four regions: CH1; CH hinge; CH 2 and CH 3 (IgG, IgA, and IgD); or CH 1, CH 2, CH 3, and CH 4 (IgM and IgE). Each CH exon consists of about 100 codons, with the hinge exon being shorter; the intronic sequences are about 300 bp each.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


