
The Special Theory of Relativity
 المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
 المصدر:
Physics 2000
المصدر:
Physics 2000
 الجزء والصفحة:
59
الجزء والصفحة:
59
 21-11-2020
21-11-2020
 1602
1602
The Special Theory of Relativity
Einstein developed his special theory of relativity from two assumptions:
1) The principle of relativity is correct.
2) Maxwell’s theory of light is correct.
As we have seen, the only way Maxwell’s theory of light can be correct and not violate the principle of relativity, is that every observer who measures the speed of light, must get the predicted answer 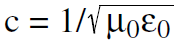 = 1 foot/nanosecond. Temporarily we will use this as the statement of Einstein’s second postulate:
= 1 foot/nanosecond. Temporarily we will use this as the statement of Einstein’s second postulate:
2a) Everyone, no matter how he or she is moving, must observe that light passes them at precisely the speed c.
Postulates (1) and (2a) salvage both the principle of relativity and Maxwell’s theory, but what else do they predict? We have seen that measurements of the speed of a pulse of light do not behave in the same way as measurements of the speed of cars on a freeway. Something peculiar seems to be happening at speeds near the speed of light. What are these peculiar things? How do we find out?
To determine the consequences of his two postulates, Einstein borrowed a technique from Galileo and used a series of thought experiments. Einstein did this so clearly, explained the consequences so well in his 1905 paper, that we will follow essentially the same line of reasoning. The main difference is that Einstein made a number of strange predictions that in 1905 were hard to believe. But these predictions were not only verified, they became the cornerstone of much of 20th century physics. We will be able to cite numerous tests of all the predictions.
 الاكثر قراءة في النظرية النسبية الخاصة
الاكثر قراءة في النظرية النسبية الخاصة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


