

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Molecular Cloning Outline
المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
الجزء والصفحة:
17-11-2020
1864
Molecular Cloning Outline
Molecular cloning provides a convenient way of breaking very large segments of DNA associated with genomes into smaller pieces that are suited to detailed analysis. Cloning involves the amplification of specific segments of DNA leading to the accumulation of large amounts of identical DNA fragments that can be used for various purposes. Classical molecular cloning employs bespoke DNA cloning vectors, which are often derived from circular DNA molecules called bacterial plasmids and bacteriophage; such recombinant vectors replicate efficiently in specialised strains of bacterial host cells, resulting in the production of multiple copies of the recombinant DNA molecule that was inserted into the vector. Before a DNA fragment can be inserted into a cloning vector, it must be prepared so that the precise DNA sequences of its ends are compatible with the ends of the vector molecule DNA sequence.
This is achieved using commercially available enzymes that cleave double-stranded DNA at specific sequences; these are known as restriction enzymes or restriction endonucleases. In Nature, restriction enzymes constitute part of the bacterial defence system by digesting double-stranded DNA from harmful bacteriophage and other foreign DNA as it enters the cell. To date, more than 3500 restriction enzymes have been identified, some of which are commercially available and used for routine molecular biology applications.If both the vector and the fragments of ‘foreign’ DNA are cut with the same restriction enzyme, such as EcoRI, which cuts at the sequence 50GAATTC30, it is a relatively straightforward procedure to join, or ligate, the two molecules because their matching ends have small overhangs with complementary base pairs (Figure ). The resulting molecule is a recombinant vector which is capable of growing in the host cell.
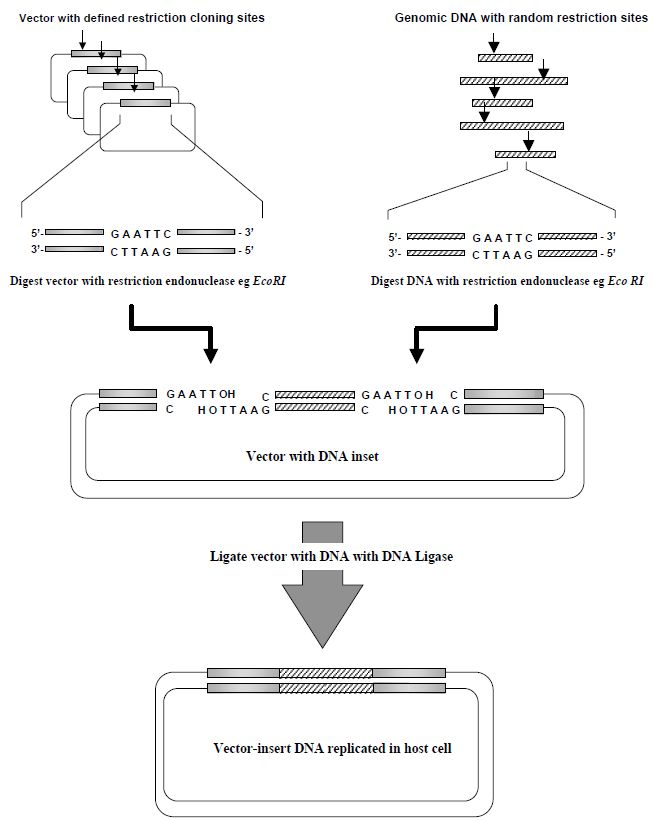
Figure : Overview of the restriction endonuclease digestion and DNA ligation process in DNA cloning.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















