

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Blood group antigens
المؤلف:
Genetics Home Reference
المصدر:
Help Me Understand Genetics
الجزء والصفحة:
15-10-2020
4073
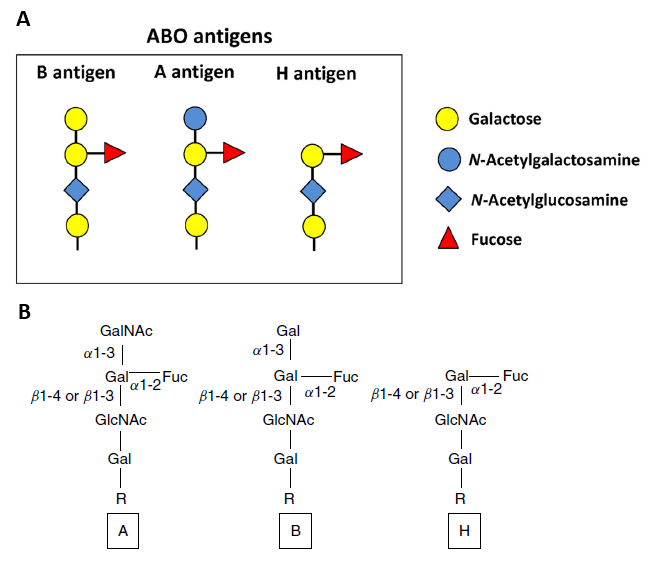
Blood group antigens
Blood is classified into different groups according to the presence or absence of molecules called antigens on the surface of every red blood cell in a person's body. Antigens determine blood type and can either be proteins or complexes of sugar molecules (polysaccharides). The genes in the blood group antigen group provide instructions for making antigen proteins. Blood group antigen proteins serve a variety of functions within the cell membrane of red blood cells. These protein functions include transporting other proteins and molecules into and out of the cell, maintaining cell structure, attaching to other cells and molecules, and participating in chemical reactions.
Blood group antigens play a role in recognizing foreign cells in the bloodstream. For example, if a person with blood type A receives a blood transfusion with blood type B, the recipient's immune system will recognize the type B cells as foreign and mount an immune response. Antibodies against type B blood cells (anti-B antibodies) are made, which attack and destroy the type B blood cells.
This sort of blood type mismatch can lead to illness. Some blood types are associated with more severe immune reactions than others. The blood type of donated cells, or tissues in the case of organ donation, is checked before being given to a recipient to prevent this immune response.
There are 29 recognized blood groups, most involving only one gene. Variations (polymorphisms) within the genes that determine blood group give rise to the different antigens for a particular blood group protein. For example, changes in a few DNA building blocks (nucleotides) in the ABO gene give rise to the A, B, and O blood types of the ABO blood group. The changes that occur in the genes that determine blood group typically affect only blood type and are not associated with adverse health conditions, although exceptions do occur.
Example of a gene in this gene group: SLC4A1, ABCG2, XK The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) provides an index of gene groups (https://www.genenames.org/data/genegroup/#!/group/454) and their member genes.
 الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















