

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Carbon-14 cycle
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
2-9-2020
1670
The Carbon-14 cycle
Radiocarbon dating (usually referred to simply as carbon-14 dating) is a radiometric dating method. It uses the naturally occurring radioisotope carbon-14 (14C) to estimate the age of carbon-bearing materials up to about 58,000 to 62,000 years old. Carbon has two stable, nonradioactive isotopes: carbon-12 (12C) and carbon-13 (13C). There are also trace amounts of the unstable radioisotope carbon-14 (14C) on Earth. Carbon-14 has a relatively short half-life of 5,730 years, meaning that the fraction of carbon-14 in a sample is halved over the course of 5,730 years due to radioactive decay to nitrogen-14. The carbon-14 isotope would vanish from Earth's atmosphere in less than a million years were it not for the constant influx of cosmic rays interacting with molecules of nitrogen (N2) and single nitrogen atoms (N) in the stratosphere. Both processes of formation and decay of carbon-14 are shown in Figure 1.
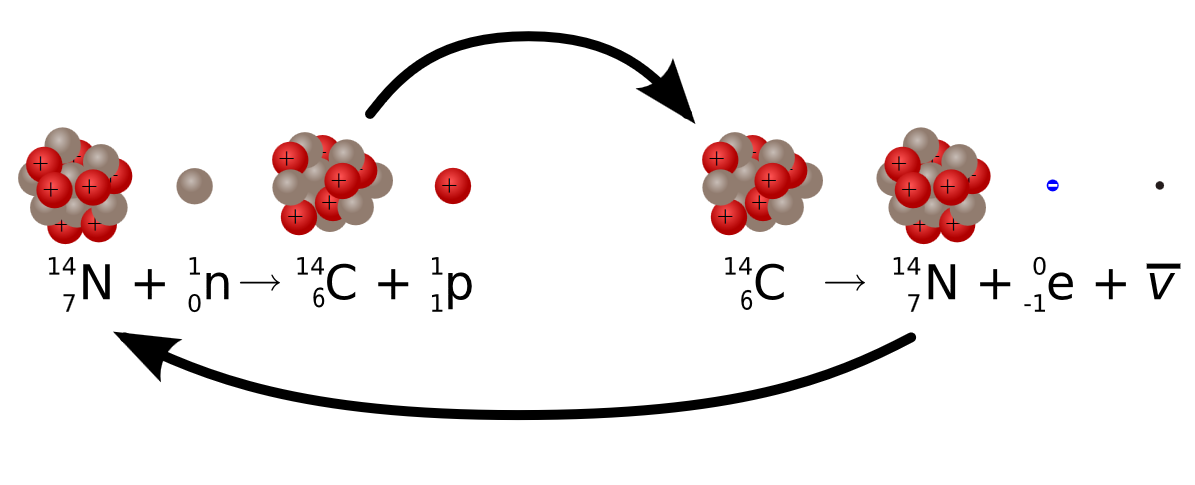
Figure 1: Diagram of the formation of carbon-14 (forward), the decay of carbon-14 (reverse). Carbon-14 is constantly be generated in the atmosphere and cycled through the carbon and nitrogen cycles. Once an organism is decoupled from these cycles (i.e., death), then the carbon-14 decays until essentially gone.
When plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic compounds during photosynthesis, the resulting fraction of the isotope 14C in the plant tissue will match the fraction of the isotope in the atmosphere (and biosphere since they are coupled). After a plants die, the incorporation of all carbon isotopes, including 14C, stops and the concentration of 14C declines due to the radioactive decay of 14C following.
This follows first-order kinetics.
where
- N0 is the number of atoms of the isotope in the original sample (at time t = 0, when the organism from which the sample was decoupled from the biosphere), and
- Nt is the number of atoms left after time t
- and k is the rate constant for the radioactive decay.
The half-life of a radioactive isotope (usually denoted by t1/2 ) is a more familiar concept than k for radioactivity, so although Equation 2 is expressed in terms of k, it is more usual to quote the value of t1/2 . The currently accepted value for the half-life of 14C is 5,730 years. This means that after 5,730 years, only half of the initial 14C will remain; a quarter will remain after 11,460 years; an eighth after 17,190 years; and so on.
The equation relating rate constant to half-life for first order kinetics is
(3)
so the rate constant is then
(4)
and Equation 1 can be rewritten as
(5)
The sample is assumed to have originally had the same 14C/12C ratio as the ratio in the atmosphere, and since the size of the sample is known, the total number of atoms in the sample can be calculated, yielding N0, the number of 14C atoms in the original sample. Measurement of N, the number of 14C atoms currently in the sample, allows the calculation of t, the age of the sample, using the Equation 5.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















