

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Generating Ionic Bonds
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
5-7-2020
1622
Generating Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds form when metals and non-metals chemically react. By definition, a metal is relatively stable if it loses electrons to form a complete valence shell and becomes positively charged. Likewise, a non-metal becomes stable by gaining electrons to complete its valence shell and become negatively charged. When metals and non-metals react, the metals lose electrons by transferring them to the non-metals, which gain them. Consequently, ions are formed, which instantly attract each other—ionic bonding.
In the overall ionic compound, positive and negative charges must be balanced, because electrons cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred. Thus, the total number of electrons lost by the cationic species must equal the total number of electrons gained by the anionic species.
Example 1 : Sodium Chloride
For example, in the reaction of Na (sodium) and Cl (chlorine), each Cl atom takes one electron from a Na atom. Therefore each Na becomes a Na+ cation and each Cl atom becomes a Cl- anion. Due to their opposite charges, they attract each other to form an ionic lattice. The formula (ratio of positive to negative ions) in the lattice is NaCl.
These ions are arranged in solid NaCl in a regular three-dimensional arrangement (or lattice):
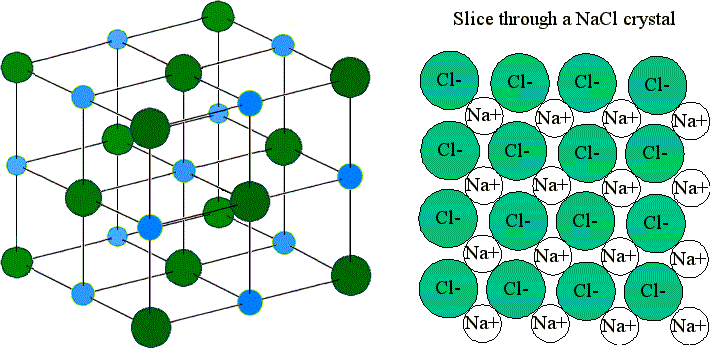
NaCl lattice. (left) 3-D structure and (right) simple 2D slice through lattes. Images used with permission from Wikipedia and Mike Blaber.
The chlorine has a high affinity for electrons, and the sodium has a low ionization energy. Thus the chlorine gains an electron from the sodium atom. This can be represented using ewis dot symbols (here we will consider one chlorine atom, rather than Cl2):
The arrow indicates the transfer of the electron from sodium to chlorine to form the Na+ metal ion and the Cl- chloride ion. Each ion now has an octet of electrons in its valence shell:
- Na+: 2s22p6
- Cl-: 3s23p6
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















