

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Not all ion-derived solids are "ionic"
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
10-5-2020
1574
Not all ion-derived solids are "ionic"
Even within the alkali halides, the role of coulombic attraction diminishes as the ions become larger and more polarizable or differ greatly in radii. This is especially true of the anions, which tend to be larger and whose electron clouds are more easily distorted. In solids composed of polyatomic ions such as (NH4)2SO4, SrClO4, NH4CO3, ion-dipole and ion-induced dipole forces may actually be stronger than the coulombic force. Higher ionic charges help, especially if the ions are relatively small. This is especially evident in the extremely high melting points of the Group 2 and higher oxides:
| MgO (magnesia) | CaO (lime) | SrO (strontia) | Al2O3 (alumina) | ZrO2 (zirconia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2830 °C | 2610 °C | 2430 °C | 2050 °C | 2715 °C |
These substances are known as refractories, meaning that they retain their essential properties at high temperatures. Magnesia, for example, is used to insulate electric heating elements and, in the form of fire bricks, to line high-temperature furnaces. No boiling points have been observed for these compounds; on further heating, they simply dissociate into their elements. Their crystal structures can be very complex, and some (notably Al2O3) can have several solid forms. Even in the most highly ionic solids there is some electron sharing, so the idea of a “pure” ionic bond is an abstraction.
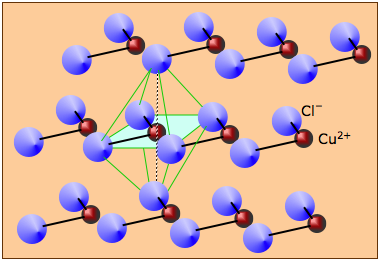
Many solids that are formally derived from ions cannot really be said to form "ionic" solids at all. For example, anhydrous copper(II) chloride consists of layers of copper atoms surrounded by four chlorine atoms in a square arrangement. Neighboring chains are offset so as to create an octahedral coordination of each copper atom. Similar structures are commonly encountered for other salts of transition metals. Similarly, most oxides and sulfides of metals beyond Group 2 tend to have structures dominated by other than ion-ion attractions.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















