

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Hydrogen Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
2-1-2020
1426
Hydrogen Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Some types of atomic nuclei act as though they spin on their axis similar to the Earth. Since they are positively charged they generate an electromagnetic field just as the Earth does. So, in effect, they will act as tiny bar magnetics. Not all nuclei act this way, but fortunately both 1H and 13C do have nuclear spins and will respond to this technique.

NMR Spectrometer
In the absence of an external magnetic field the direction of the spin of the nuclei will be randomly oriented (see figure below left). However, when a sample of these nuclei is place in an external magnetic field, the nuclear spins will adopt specific orientations much as a compass needle responses to the Earth’s magnetic field and aligns with it. Two possible orientations are possible, with the external field (i.e. parallel to and in the same direction as the external field) or against the field (i.e. antiparallel to the external field). See figure below right.
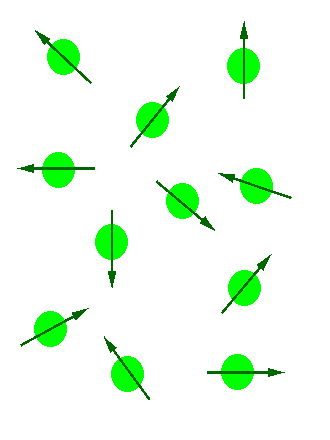
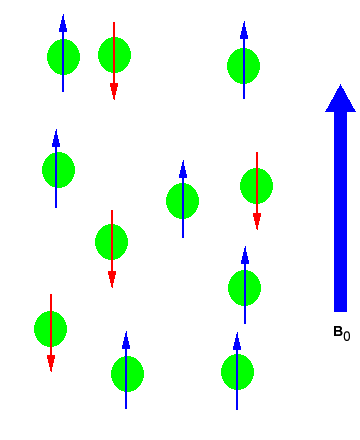
Figure 1: (Left) Random nuclear spin without an external magnetic field. (Right)Ordered nuclear spin in an external magnetic field
If the ordered nuclei are now subjected to EM radiation of the proper frequency the nuclei aligned with the field will absorb energy and "spin-flip" to align themselves against the field, a higher energy state. When this spin-flip occurs the nuclei are said to be in "resonance" with the field, hence the name for the technique, Nuclear Magentic Resonance or NMR.
The amount of energy, and hence the exact frequency of EM radiation required for resonance to occur is dependent on both the strength of the magnetic field applied and the type of the nuclei being studied. As the strength of the magnetic field increases the energy difference between the two spin states increases and a higher frequency (more energy) EM radiation needs to be applied to achieve a spin-flip (see image below).
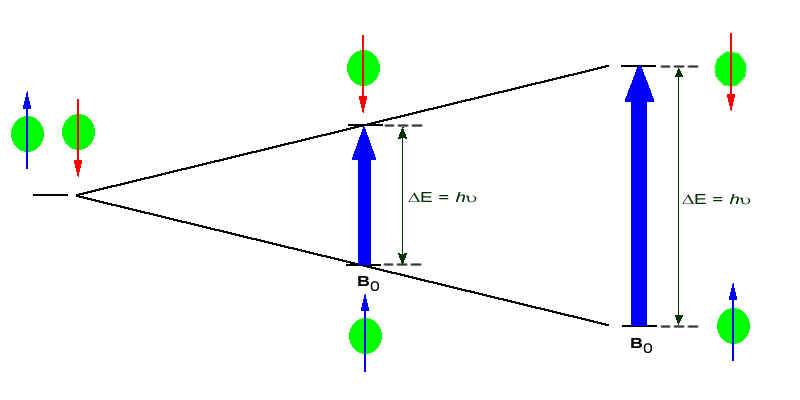
Superconducting magnets can be used to produce very strong magnetic field, on the order of 21 tesla (T). Lower field strengths can also be used, in the range of 4 - 7 T. At these levels the energy required to bring the nuclei into resonance is in the MHz range and corresponds to radio wavelength energies, i.e. at a field strength of 4.7 T 200 MHz bring 1H nuclei into resonance and 50 MHz bring 13C into resonance. This is considerably less energy then is required for IR spectroscopy, ~10-4 kJ/mol versus ~5 - ~50 kJ/mol.
1H and 13C are not unique in their ability to undergo NMR. All nuclei with an odd number of protons (1H, 2H, 14N, 19F, 31P ...) or nuclei with an odd number of neutrons (i.e. 13C) show the magnetic properties required for NMR. Only nuclei with even number of both protons and neutrons (12C and 16O) do not have the required magnetic properties.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















