

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
SN1 Mechanism
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
1-8-2019
1728
SN1 Mechanism
The first order kinetics of SN1 reactions suggests a two-step mechanism in which the rate-determining step consists of the ionization of the alkyl halide, as shown in the diagram below. In this mechanism, a carbocation is formed as a high-energy intermediate, and this species bonds immediately to nearby nucleophiles. If the nucleophile is a neutral molecule, the initial product is an "onium" cation, as drawn above for t-butyl chloride, and presumed in the energy diagram. In evaluating this mechanism, we may infer several outcomes from its function.
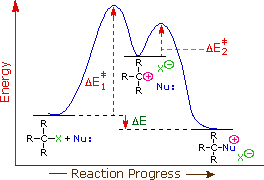
The only reactant that is undergoing change in the first (rate-determining) step is the alkyl halide, so we expect such reactions would be unimolecular and follow a first-order rate equation. Hence the name SN1 is applied to this mechanism.
- Since nucleophiles only participate in the fast second step, their relative molar concentrations rather than their nucleophilicities should be the primary product-determining factor. If a nucleophilic solvent such as water is used, its high concentration will assure that alcohols are the major product. Recombination of the halide anion with the carbocation intermediate simply reforms the starting compound. Note that SN1 reactions in which the nucleophile is also the solvent are commonly called solvolysis reactions. The hydrolysis of t-butyl chloride is an example.
- The Hammond postulate suggests that the activation energy of the rate-determining first step will be inversely proportional to the stability of the carbocation intermediate. The stability of carbocations was discussed earlier, and a qualitative relationship is given below.
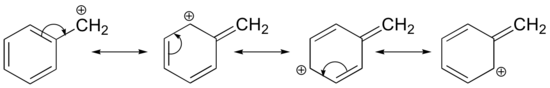
Benzyl Carbocation
|
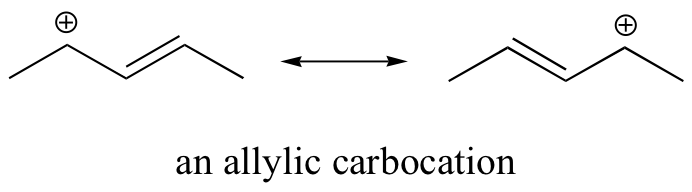
Consequently, we expect that 3º-alkyl halides will be more reactive than their 2º and 1º-counterparts in reactions that follow an SN1 mechanism. This is opposite to the reactivity order observed for the SN2 mechanism. Allylic and benzylic halides are exceptionally reactive by either mechanism.
Fourth, in order to facilitate the charge separation of an ionization reaction, as required by the first step, a good ionizing solvent will be needed. Two solvent characteristics will be particularly important in this respect. The first is the ability of solvent molecules to orient themselves between ions so as to attenuate the electrostatic force one ion exerts on the other. This characteristic is related to the dielectric constant, ε, of the solvent. Solvents having high dielectric constants, such as water (ε=81), formic acid (ε=58), dimethyl sulfoxide (ε=45) & acetonitrile (ε=39) are generally considered better ionizing solvents than are some common organic solvents such as ethanol (ε=25), acetone (ε=21), methylene chloride (ε=9) & ether (ε=4). The second factor is solvation, which refers to the solvent's ability to stabilize ions by encasing them in a sheath of weakly bonded solvent molecules. Anions are solvated by hydrogen-bonding solvents, as noted earlier. Cations are often best solvated by nucleophilic sites on a solvent molecule (e.g. oxygen & nitrogen atoms), but in the case of carbocations these nucleophiles may form strong covalent bonds to carbon, thus converting the intermediate to a substitution product. This is what happens in the hydrolysis reactions described above.
Fifth, the stereospecificity of these reactions may vary. The positively-charged carbon atom of a carbocation has a trigonal (flat) configuration (it prefers to be sp2 hybridized), and can bond to a nucleophile equally well from either face. If the intermediate from a chiral alkyl halide survives long enough to encounter a random environment, the products are expected to be racemic (a 50:50 mixture of enantiomers). On the other hand, if the departing halide anion temporarily blocks the front side, or if a nucleophile is oriented selectively at one or the other face, then the substitution might occur with predominant inversion or even retention of configuration.
Just as with SN2 reactions, the nucleophile, solvent and leaving group also affect SN1 (Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution) reactions. Polar protic solvents have a hydrogen atom attached to an electronegative atom so the hydrogen is highly polarized. Polar aprotic solvents have a dipole moment, but their hydrogen is not highly polarized. Polar aprotic solvents are not used in SN1 reactions because some of them can react with the carbocation intermediate and give you an unwanted product. Rather, polar protic solvents are preferred.
 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















