

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Photochemistry
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
29-8-2018
2030
Photochemistry
The study of chemical reactions, isomerizations and physical behavior that may occur under the influence of visible and/or ultraviolet light is called Photochemistry. Two fundamental principles are the foundation for understanding photochemical transformations:
• The first law of photochemistry, the Grotthuss-Draper law, states that light must be absorbed by a compound in order for a photochemical reaction to take place.
• The second law of photochemistry, the Stark-Einstein law, states that for each photon of light absorbed by a chemical system, only one molecule is activated for subsequent reaction. This "photoequivalence law" was derived by Albert Einstein during his development of the quantum (photon) theory of light.
efficiency with which a given photochemical process occurs is given by its Quantum Yield (Φ). Since many photochemical reactions are complex, and may compete with unproductive energy loss, the quantum yield is usually specified for a particular event. Thus, we may define quantum yield as "the number of moles of a stated reactant disappearing, or the number of moles of a stated product produced, per einstein of monochromatic light absorbed.", where an einstein is one mole of photons. For example, irradiation of acetone with 313 nm light (3130 Å ) gives a complex mixture of products, as shown in the following diagram. The quantum yield of these products is less than 0.2, indicating there are radiative (fluorescence & phosphorescence) and non-radiative return pathways (green arrow). The primary photochemical reaction is the homolytic cleavage of a carbon-carbon bond shown in the top equation. Here the asterisk represents an electronic excited state, the nature of which will be defined later.
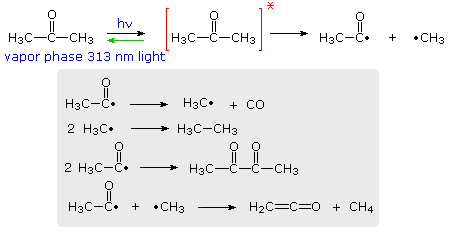
Several secondary radical reactions then follow (shown in the gray box), making it difficult to assign a quantum yield to the primary reaction. The biacetyl product, formed in the third reaction, may itself be excited by light or accept excitation energy from an excited acetone molecule, further complicating this process.
By comparison, the light induced chlorination of methane, or other alkanes, has a large quantum yield, often near 106, because of the secondary chain reactions that follow the primary cleavage of the Cl-Cl bond.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















