

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Carbon NMR Spectroscopy
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
13-8-2018
3060
Carbon NMR Spectroscopy
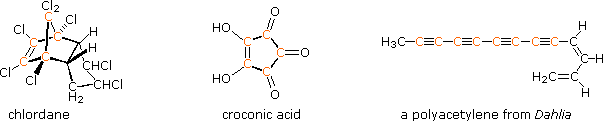
The power and usefulness of 1H nmr spectroscopy as a tool for structural analysis should be evident from the past discussion. Unfortunately, when significant portions of a molecule lack C-H bonds, no information is forthcoming. Examples include polychlorinated compounds such as chlordane, polycarbonyl compounds such as croconic acid, and compounds incorporating triple bonds (structures below, orange colored carbons).
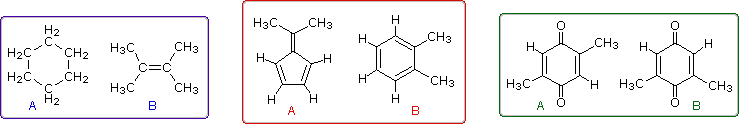
Even when numerous C-H groups are present, an unambiguous interpretation of a proton nmr spectrum may not be possible. The following diagram depicts three pairs of isomers (A & B) which display similar proton nmr spectra. Although a careful determination of chemical shifts should permit the first pair of compounds (blue box) to be distinguished, the second and third cases (red & green boxes) might be difficult to identify by proton nmr alone.
These difficulties would be largely resolved if the carbon atoms of a molecule could be probed by nmr in the same fashion as the hydrogen atoms. Since the major isotope of carbon (12C) has no spin, this option seems unrealistic. Fortunately, 1.1% of elemental carbon is the 13C isotope, which has a spin I = 1/2, so in principle it should be possible to conduct a carbon nmr experiment. It is worth noting here, that if much higher abundances of 13C were naturally present in all carbon compounds, proton nmr would become much more complicated due to large one-bond coupling of 13C and 1H.
Many obstacles needed to be overcome before carbon nmr emerged as a routine tool :
i) As noted, the abundance of 13C in a sample is very low (1.1%), so higher sample concentrations are needed.
ii) The 13C nucleus is over fifty times less sensitive than a proton in the nmr experiment, adding to the previous difficulty.
iii) Hydrogen atoms bonded to a 13C atom split its nmr signal by 130 to 270 Hz, further complicating the nmr spectrum.
The most important operational technique that has led to successful and routine 13C nmr spectroscopy is the use of high-field pulse technology coupled with broad-band heteronuclear decoupling of all protons. The results of repeated pulse sequences are accumulated to provide improved signal strength. Also, for reasons that go beyond the present treatment, the decoupling irradiation enhances the sensitivity of carbon nuclei bonded to hydrogen.
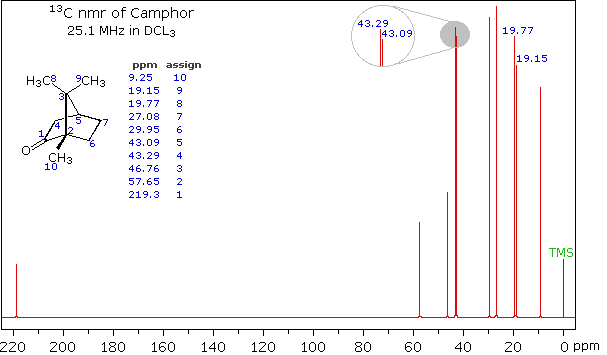
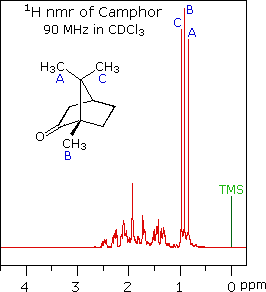
When acquired in this manner, the carbon nmr spectrum of a compound displays a single sharp signal for each structurally distinct carbon atom in a molecule (remember, the proton couplings have been removed). The spectrum of camphor, shown on the left below, is typical. Furthermore, a comparison with the 1H nmr spectrum on the right illustrates some of the advantageous characteristics of carbon nmr. The dispersion of 13C chemical shifts is nearly twenty times greater than that for protons, and this together with the lack of signal splitting makes it more likely that every structurally distinct carbon atom will produce a separate signal. The only clearly identifiable signals in the proton spectrum are those from the methyl groups. The remaining protons have resonance signals between 1.0 and 2.8 ppm from TMS, and they overlap badly thanks to spin-spin splitting.
Unlike proton nmr spectroscopy, the relative strength of carbon nmr signals are not normally proportional to the number of atoms generating each one. Because of this, the number of discrete signals and their chemical shifts are the most important pieces of evidence delivered by a carbon spectrum. The general distribution of carbon chemical shifts associated with different functional groups is summarized in the following chart. Bear in mind that these ranges are approximate, and may not encompass all compounds of a given class.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















