

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Silicon halides
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 363
6-2-2018
1761
Silicon halides
Many fluorides and chlorides of Si are known, but we confine our discussion to SiF4 and SiCl4 and some of their derivatives. Silicon and Cl2 react to give SiCl4, and SiF4 can be obtained by fluorination of SiCl4 using SbF3, or by reaction 1.1.
 (1.1)
(1.1)
Both SiF4 and SiCl4 are molecular with tetrahedral structures. They react readily with water, but the former is only partially hydrolysed (compare equations 1.2 and 1.3). Controlled hydrolysis of SiCl4 results in the formation of (Cl3Si)2O, through the intermediate SiCl3OH.
 (1.2)
(1.2)
 (1.3)
(1.3)
The reaction between equimolar amounts of neat SiCl4 and SiBr4 at 298K leads to an equilibration mixture of SiCl4, SiBrCl3, SiBr2Cl2, SiBr3Cl and SiBr4 which can be separated by fractional distillation. The Lewis base N-methylimidazole (MeIm) reacts with SiCl4 and SiBr2Cl2 to give trans-[SiCl2(MeIm)4]2 (Figure 1.1a) as the chloride and bromide salts respectively. This provides a means of stabilizing an [SiCl2]2 cation. The formation of [SiF6]2-, the hexafluorosilicate ion (Figure 1.1b), illustrates the ability of Si to act as an F- acceptor and increase its coordination number beyond 4.
Hexafluorosilicates are best prepared by reactions of SiF4 with metal fluorides in aqueous HF; the K and Ba2+ salts are sparingly soluble. In aqueous solution, fluorosilicic acid is a strong acid, but pure H2SiF6 has not been isolated. The [SiF5]- ion (Figure 1.1c) is formed in the reaction of SiO2 with aqueous HF, and may be isolated as a tetraalkylammonium ion. Silicon tetrachloride does not react with alkali metal chlorides, although lattice energy considerations suggest that it might be possible to stabilize the [SiCl6]2- ion using a very large quaternary ammonium cation.
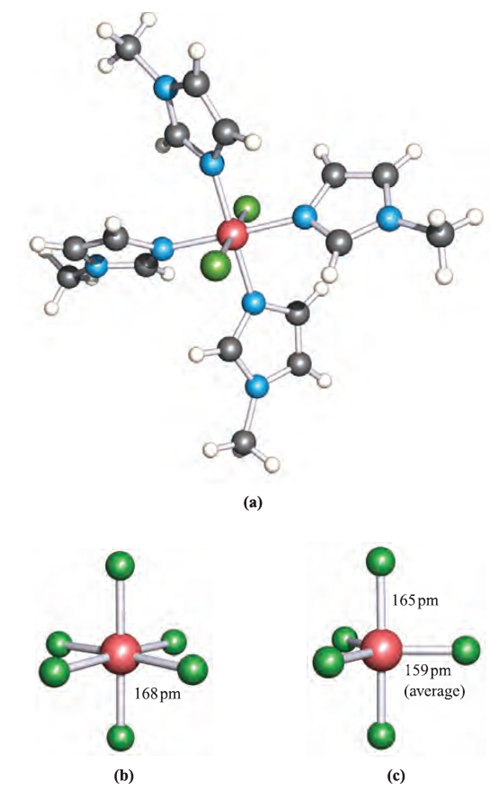
Fig. 1.1 Solid state structures (X-ray diffraction) of (a) trans-[SiCl2(MeIm)4]2 from the salt [SiCl2(MeIm)4]Cl2:3CHCl3 (MeIm = N-methylimidazole) [K. Hensen et al. (2000) J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., p. 473], (b) octahedral [SiF6]2-, determined for the salt [C(NH2)3]2[SiF6] [A. Waskowska (1997) Acta Crystallogr., Sect. C, vol. 53, p. 128] and (c) trigonal bipyramidal [SiF5]-, determined for the compound [Et4N][SiF5] [D. Schomburg et al. (1984) Inorg.