
‘Normal’ spinel and ‘inverse’ spinel lattices
 المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
 المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 316
الجزء والصفحة:
p 316
 29-1-2018
29-1-2018
 3229
3229
‘Normal’ spinel and ‘inverse’ spinel lattices
A large group of minerals called spinels have the general formula AB2X4 in which X is most commonly oxygen and the oxidation states of metals A and B are +2 and +3 respectively; examples include MgAl2O4 (spinel, after which this structural group is named), FeCr2O4 (chromite) and Fe3O4 (magnetite, a mixed Fe(II), Fe(III) oxide). The spinel family also includes sulfides, selenides and tellurides, and may contain metal ions in the +4 and +2 oxidation states, e.g. TiMg2O4, usually written as Mg2TiO4. Our discussion below focuses on spinel-type compounds containing A2+ and B3+ ions.
The spinel lattice is not geometrically simple but can be considered in terms of a cubic close-packed array of O2- ions with one-eighth of the tetrahedral holes occupied by A2+ ions and half of the octahedral holes occupied by B3+ ions.
The unit cell contains eight formula units, i.e. [AB2X4]8. Some mixed metal oxides AB2X4 in which at least one of the metals is a d-block element (e.g. CoFe2O4) possess an inverse spinel structure which is derived from the spinel lattice by exchanging the sites of the A2+ ions with half of the B3+ ions. The occupation of octahedral sites may be ordered or random, and structure types cannot be simply partitioned into ‘normal’ or ‘inverse’. A parameter λ is used to provide information about the distribution of cations in the interstitial sites of the close-packed array of X2- ions; λ indicates the proportion of B3+ ions occupying tetrahedral holes. For a normal spinel, λ = 0; for an inverse spinel, λ = 0:5. Thus, for MgAl2O4, λ = 0, and for CoFe2O4, λ = 0:5. Other spineltype compounds have values of λ between 0 and 0.5; for example, for MgFe2O4, λ = 0:45 and for NiAl2O4, λ = 0:38.
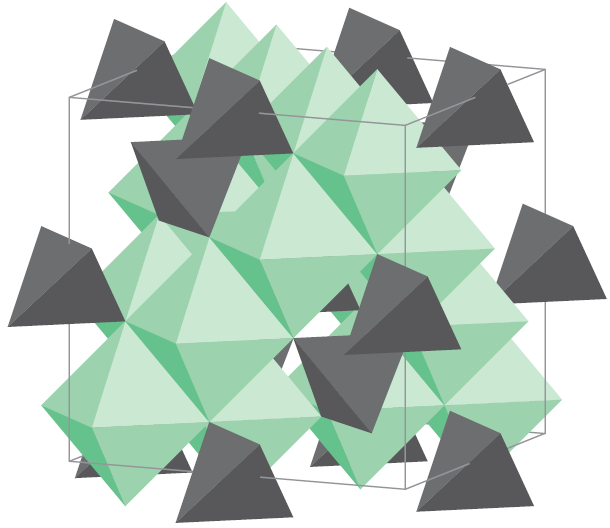
The inverse spinel structure of Fe3O4 showing the unit cell and the tetrahedral and octahedral environments of the Fe centres. The vertex of each tetrahedron and octahedron is occupied by an O atom.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


