

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Reactivity of the group 2 metals
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 279
17-1-2018
2241
Reactivity of the group 2 metals
Beryllium and magnesium are passivated and are kinetically inert to O2 and H2O at ambient temperatures. However, Mg amalgam liberates H2 from water, since no coating of oxide forms on its surface; Mg metal reacts with steam or hot water.
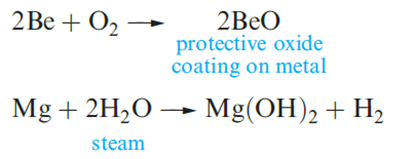
Beryllium and magnesium dissolve readily in non-oxidizing acids; magnesium is attacked by nitric acid, whereas beryllium reacts with dilute HNO3 but is passivated by concentrated nitric acid. Magnesium does not react with aqueous alkali, whereas Be forms an amphoteric hydroxide.
The metals Ca, Sr and Ba exhibit similar chemical behaviours, generally resembling, but being slightly less reactive than, Na. They react with water and acids liberating H2, and the similarity with Na extends to dissolution in liquid NH3 to give blue solutions containing solvated electrons. From these solutions, it is possible to isolate hexaammines, [M(NH3)6] (M = Ca, Sr, Ba), but these slowly decompose to amides .
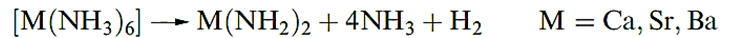
When heated, all the group 2 metals combine with O2, N2, sulfur or halogens.
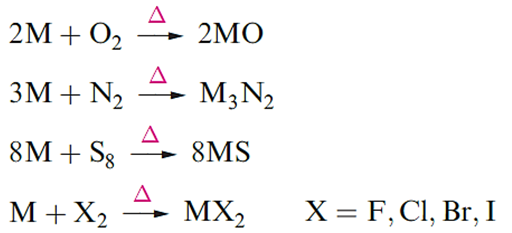
Differences between the first and later members of group 2 are illustrated by the formation of hydrides and carbides. When heated with H2, Ca, Sr and Ba form saline hydrides, MH2, but Mg reacts only under high pressure. In contrast, BeH2 is prepared from beryllium alkyls. Beryllium combines with carbon at high temperatures to give Be2C which possesses an antifluorite lattice. The other group 2 metals form carbides MC2 which contain the [C≡C]2- ion, and adopt NaCl lattices that are elongated along one axis. Whereas Be2C reacts with water the carbides of the later metals hydrolyse to yield C2H2. CaH2 is used as a drying agent but its reaction with water is highly exothermic.
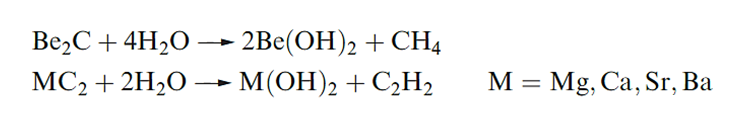
The carbide Mg2C3 (which contains the linear [C3]4- ion isoelectronic with CO2) is formed by heating MgC2, or by reaction of Mg dust with pentane vapour at 950 K. Reaction of Mg2C3 with water produces MeC≡CH.
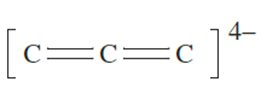
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















