

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Physical properties of the group 13 elements
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 297
5-4-2017
2590
Physical properties of the group 13 elements
Table1.1 lists selected physical properties of the group 13 elements. Despite the discussion of ionization energies that follows, there is no evidence for the formation of free M3+ ions in compounds of the group 13 elements under normal conditions, other than, perhaps, some trifluorides. Electronic configurations and oxidation States While the elements have an outer electronic configuration ns2np1 and a larger difference between IE1 and IE2 than between IE2 and IE3 (i.e. comparing the removal of a p with that of an s electron), the relationships between the electronic structures of the group 13 elements and those of the preceding noble gases are more complex than for the group 1 and 2 elements . For Ga and In, the electronic structures of the species formed after the removal of three valence electrons are [Ar]3d10 and [Kr]4d10 respectively, while for Tl, the corresponding species has the configuration [Xe]4f 145d10. Thus, whereas for B and Al, the value of IE4 (Table1.1) refers to the removal of an electron from a noble gas configuration, this is not the case for the three later elements; the difference between IE3 and IE4 is not nearly so large for Ga, In and Tl as for B and Al. On going down group 13, the observed discontinuities in values of IE2 and IE3, and the differences between them (Table1.1), originate in the failure of the d and f electrons (which have a low screening power, see Section 1.7) to compensate for the increase in nuclear charge. This failure is also reflected in the relatively small difference between values of rion for Al3+ and Ga3+. For Tl, relativistic effects are also involved.
Table1.1 Some physical properties of the group 13 elements, M, and their ions.
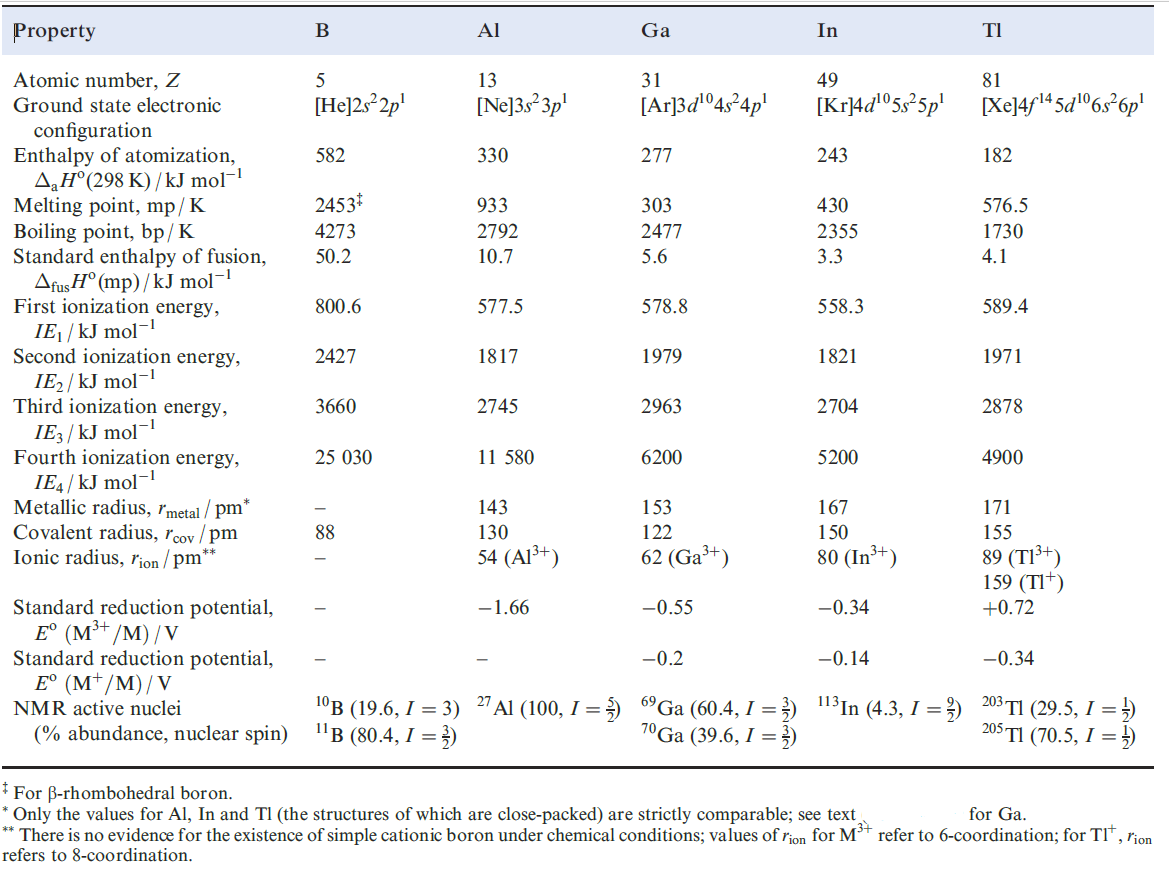
On descending group 13, the trend in IE2 and IE3 shows increases at Ga and Tl (Table1.1), and this leads to a marked increase in stability of the +1 oxidation state for these elements. In the case of Tl (the only salt-like trihalide of which is TlF3), this is termed the thermodynamic 6s inert pair effect so called to distinguish it from the stereochemical inert pair effect mentioned. Similar effects are seen for Pb (group 14) and Bi (group 15), for which the most stable oxidation states are +2 and +3 respectively, rather than 4 and 5. The inclusion in Table1.1 of Eo values for the M3+/M and M/M redox couples for the later group 13 elements reflects the variable accessibility of the M state within the group.
Although an oxidation state of +3 (and for Ga and Tl, 1) is characteristic of a group 13 element, most of the group 13 elements also form compounds in which a formal oxidation state of +2 is suggested, e.g. B2Cl4 and GaCl2. However, caution is needed. In B2Cl4, the +2 oxidation state arises because of the presence of a B_B bond, and GaCl2 is the mixed oxidation state species Ga[GaCl4].
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















