

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Compounds of krypton and radon
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 501
5-3-2017
1535
Compounds of krypton and radon
The only binary compound containing Kr is KrF2. It is a colourless solid which decomposes >250 K, and is best prepared by UV irradiation of a mixture of Kr and F2 (4 :1 molar ratio) at 77 K. Krypton difluoride is dimorphic. The low-temperature phase, α-KrF2, is isomorphous with XeF2 (Figure 1.1a). The structure of the β-form of KrF2 is shown in Figure 1.1b. The phase transition from β- to α- KrF2 occurs below 193 K. Krypton difluoride is much less stable than XeF2.
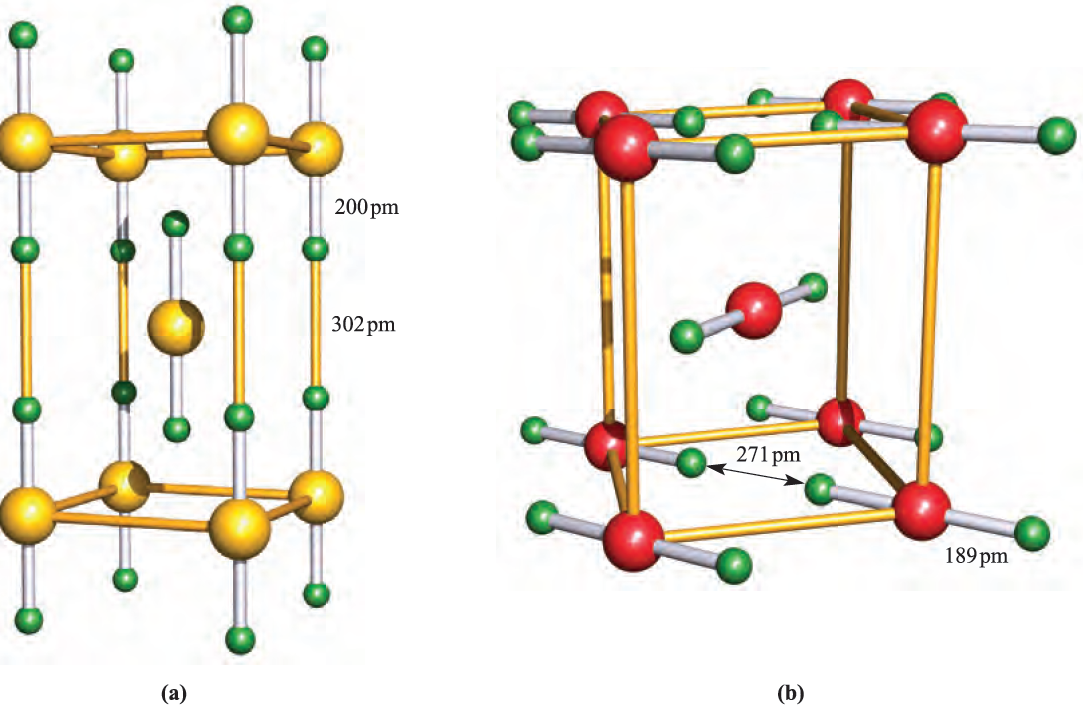
Fig. 1.1 Unit cells of (a) XeF2 and (b) β-KrF2 showing the arrangements and close proximity of molecular units. Colour code: Xe, yellow; Kr, red; F, green.
It is rapidly hydrolysed by water and dissociates into Kr and F2 at 298K (∆fHo(298K) = 60.2 kJ mol-1). We have already exemplified the use of KrF2 as a powerful oxidizing agent in the syntheses of [XeF5][AgF4] and [Xe2F11]2[NiF6] (Section 1.1). Krypton difluoride reacts with a number of pentafluorides, MF5 (typically in anhydrous HF or BrF5 at low temperature), to form [KrF][MF6]- (M=As, Sb, Bi, Ta), [KrF][M2F11]- (M=Sb, Ta, Nb) and [Kr2F3][MF6]- (M=As, Sb, Ta). In the solid state, the [KrF]+ ion in [KrF]+[MF6]- (M=As, Sb, Bi) is strongly associated with the anion (e.g. structure 1.1). The [Kr2F3] ion (1.1) is structurally similar to [Xe2F3] (17.5). The oxidizing and fluorinating powers of KrF2 are illustrated by its reaction with metallic gold to give [KrF]+[AuF6]-. Few compounds are known that contain Kr bonded to elements other than F. The reactions between KrF2, RC≡N (e.g. R = H, CF3) and AsF5 in liquid HF or BrF5 yield [(RCN)KrF]+[AsF6]- with Kr_N bond formation, and Kr_O bond formation has been observed in the reaction of KrF2 and B)OTeF5(3 to give Kr)OTeF5(2. Radon is oxidized by halogen fluorides (e.g. ClF, ClF3) to the non-volatile RnF2; the latter is reduced by H2 at 770 K, and is hydrolysed by water in a analogous manner to XeF2 .
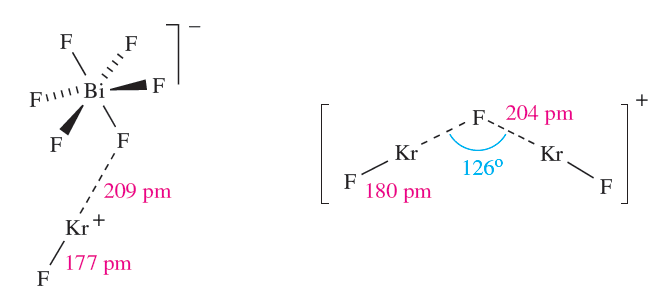
(1.1) (1.1)
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















