

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Group 13: Boron
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 512
2-3-2017
1766
Group 13: Boron
Organoboranes of type R3B can be prepared by reaction 1.1, or by the hydroboration reaction mentioned above.
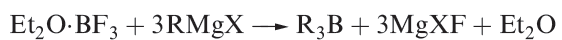 (1.1)
(1.1)
Trialkylboranes are monomeric and inert towards water, but are pyrophoric; the triaryl compounds are less reactive. Both sets of compounds contain planar 3-coordinate B and act as Lewis acids towards amines and carbanions. Reaction 1.2 shows an important example; sodium tetraphenylborate is water-soluble but salts of larger monopositive cations (e.g. K) are insoluble. This makes Na[BPh4] useful in the precipitation of large metal ions.
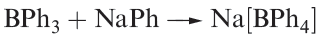 (1.2)
(1.2)
Compounds of the types R2BCl and RBCl2 can be prepared by transmetallation reactions (e.g. equation 1.3) and are synthetically useful (e.g. reaction 1.4).
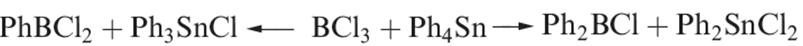 (1.3)
(1.3)
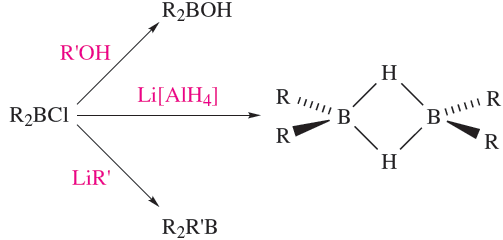 (1.4)
(1.4)
The bonding in R2B(µ-H)2BR2 can be described in a similar manner to that in B2H6. An important member of this family is 1.1, commonly known as 9-BBN, which is used for the regioselective reduction of ketones, aldehydes, alkynes and nitriles.
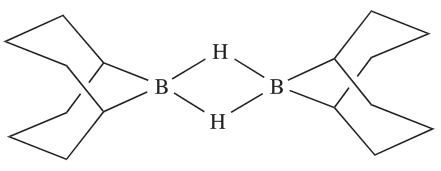 (1.1)
(1.1)
By using bulky organic substituents (e.g. mesityl = 2,4,6-Me3C6H2), it is possible to stabilize compounds of type R2B_BR2. These should be contrasted with X2B_BX2 where X = halogen or NR2 in which there is X → B π- overlap. Two-electron reduction of R2B_BR2 gives [R2B=BR2]2-, an isoelectronic analogue of an alkene. The planar B2C4 framework has been confirmed by X-ray diffraction for Li2[B2(2,4,6-Me3C6H2)3Ph], although there is significant interaction between the B=B unit and two Li centres. The shortening of the B_B bond on going from B2(2,4,6-Me3C6H2)3Ph (171pm) to [B2(2,4,6-Me3C6H2)3Ph]2- (163 pm) is less than might be expected and this observation is attributed to the large Coulombic repulsion between the two B- centres.
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















