النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Rates of Growth
المؤلف:
AN INTRODUCTION TO PLANT BIOLOGY-1998
المصدر:
JAMES D. MAUSETH
الجزء والصفحة:
18-10-2016
2047
Rates of Growth
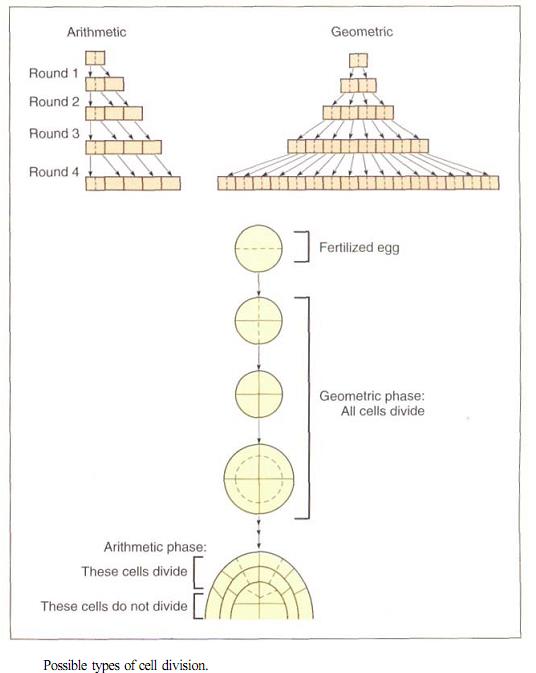
An organism, or a part of an organism, can produce more cells in a variety of ways. The two ways that are most important for you to understand are called arithmetic and geometric increase.
In arithmetic increase, only one cell is allowed to divide. Of the two resulting progeny cells, one continues to be able to divide but the other undergoes cell cycle arrest and begins to develop, differentiate, and mature. After each round of cell division, only a single cell remains capable of division and one new body cell exists. For example, starting with a single cell, after round 1 of cell division there is one dividing cell and one body cell, after round 2 there are two body cells, after round 3 there are three, and so on. To obtain a plant body containing one million cells (which would be a very small body), the plant's single dividing cell would undergo one million rounds of nuclear and cellular division. If each round requires one day, this type of arithmetic increase would require one million days, or 2739.7 years. As you can imagine, this arithmetic rate of increase is too slow to ever produce an entire plant or animal. However, it is capable of producing the small number of cells present in very small parts of plants. For example, the hairs on many leaves and stems consist of just a single row of cells produced by the division of the basal cell, the cell at the bottom of the hair next to the other epidermal cells. The hair may contain five to ten cells, so all its cells could be produced in just five to ten days by divisions of the basal cell; this would be quick compared with the rest of leaf development, which might take weeks or months.
An alternative pattern of growth by cell division, geometric increase, results if all cells of the organism or tissue are active mitotically. Again starting with a single cell, after round 1 of cell division, there are two cells capable of cell division, after round 2 there are four, after round 3 there are eight, and so on. The number of cells increases extremely rapidly and can be calculated as a power of 2. After round 3 there are 23 = 8 cells, and after round 10 there are 210 = 1024 cells (these calculations should be easy for you on any pocket calculator). Notice that after round 20 there are already 220 = 1,048,576 cells. If, as in our previous example, each round of cell division re-quires one day, it now takes the plant only 20 days, not thousands of years, to reach a size of one million cells. With geometric in-crease, a large plant or animal body can be produced quickly.
In fact, geometric growth is common in animals but rarely occurs in plants except when they are extremely young and small. The problem is that in plants, dividing cells are typically simple and do not carry out many of the specialized metabolic processes necessary for plant survival. They cannot be the tough, hard fiber cells that make wood strong enough to hold up a tree; they cannot be the waxy, waterproofing cells of the plant's skin that protect it from fungi, bacteria, and loss of water.
Plants grow by a combination of arithmetic and geometric increase. A young, em-bryonic plant grows geometrically and rap-idly, with all its cells dividing. Then cell division becomes restricted to certain cells at example, each round of cell division re-quires one day, it now takes the plant only 20 days, not thousands of years, to reach a size of one million cells. With geometric in-crease, a large plant or animal body can be produced quickly.
In fact, geometric growth is common in animals but rarely occurs in plants except when they are extremely young and small. The problem is that in plants, dividing cells are typically simple and do not carry out many of the specialized metabolic processes necessary for plant survival. They cannot be the tough, hard fiber cells that make wood strong enough to hold up a tree; they cannot be the waxy, waterproofing cells of the plant's skin that protect it from fungi, bacteria, and loss of water. the tips of roots and shoots. After this point, growth is of the slower arithmetic type, but some of the new cells that are produced can develop into their mature condition and begin carrying out specialized types of metabolism. Plants are thus a mixture of older, mature cells and young, dividing cells.