

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The tetrahedral crystal field
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
الجزء والصفحة:
2th ed p 562
19-8-2016
1505
The tetrahedral crystal field
So far we have restricted the discussion to octahedral complexes; we now turn to the tetrahedral crystal field. Figure 1.1 shows a convenient way of relating a tetrahedron to a Cartesian axis set. With the complex in this orientation, none of the metal d orbitals points exactly at the ligands, but the dxy, dyz and dxz orbitals come nearer to doing so than the dz2 and dx2-y2 orbitals. For a regular tetrahedron, the splitting of the d orbitals is inverted compared with that for a regular octahedral structure, and the energy difference (Δtet) is smaller.

Fig. 1.1 The relationship between a tetrahedral ML4 complex and a cube; the cube is readily related to a Cartesian axis set. The ligands lie between the x, y and z axes; compare this with an octahedral complex, where the ligands lie on the axes.
If all other things are equal (and of course, they never are), the relative splittings Δoct and Δtet are related by equation 1.1.
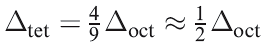 (1.1)
(1.1)
Figure 1.2 compares crystal field splitting for octahedral and tetrahedral fields; remember, the subscript g in the symmetry labels is not needed in the tetrahedral case.
Since Δtet is significantly smaller than Δoct , tetrahedral complexes are high-spin. Also, since smaller amounts of energy are needed for an t2←e transition (tetrahedral) than for an eg←t2g transition (octahedral), corresponding octahedral and tetrahedral complexes often have different colours. Jahn–Teller effects in tetrahedral complexes are illustrated by distortions in d9 (e.g. [CuCl4]2-) and high-spin d4 complexes. A particularly strong structural distortion is observed in [FeO4]4-.
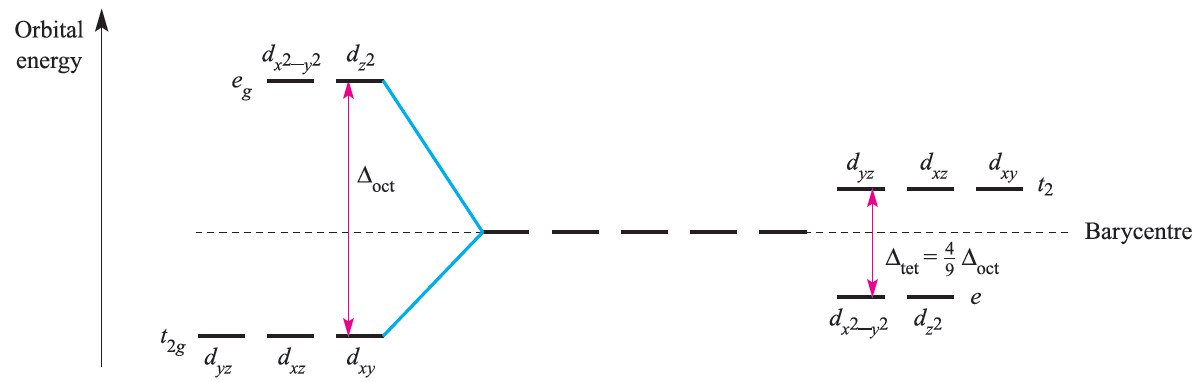
Fig. 1.2 Crystal field splitting diagrams for octahedral (left-hand side) and tetrahedral (right-hand side) fields.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















