

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Enterobacteriaceae
المؤلف:
Fritz H. Kayser
المصدر:
Medical Microbiology -2005
الجزء والصفحة:
6-3-2016
3560
Enterobacteriaceae
Overview
The most important bacterial family in human medicine is the Enterobacteriaceae. This family includes genera and species that cause well-defined diseases with typical clinical symptoms (typhoid fever, dysentery, plague) as well as many opportunists that cause mainly nosocomial infections (urinary tract infections, pneumonias, wound infections, sepsis). Enterobacteriaceae are Gram-negative, usually motile, facultatively anaerobic rod bacteria. The high levels of metabolic activity observed in them are made use of in identification procedures. The species are subdivided into epidemiologically
significant samovars based on O, H, and K antigens. The most important pathogenicity factors of Enterobacteriaceae are colonizing factors, invasins, endotoxin, and various exotoxins. Enterobacteriaceae are the most significant contributors to intestinal infections, which are among the most frequent diseases of all among the developing world populace.
Definition and significance. Together with the families Vibrionaceae and others , the Enterobacteriaceae form the group of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic rod bacteria. Their natural habitat is the intestinal tract of humans and animals. Some species cause characteristic diseases. While others are facultatively pathogenic, they are still among the bacteria most frequently isolated as pathogens (e.g., E. coli). They are often responsible for nosocomial diseases (see p. 343ff.).
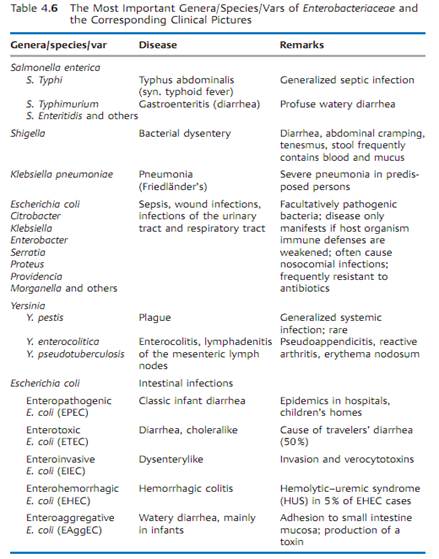
Taxonomy. The taxonomy of the Enterobacteriaceae has seen repeated changes in recent decades and has doubtless not yet assumed its final form. The family includes 41 genera with hundreds of species. Table 4.6 provides an overview of the most important Enterobacteriaceae in the field of human medicine.
The taxonomic system applied to Enterobacteriaceae is based on varying patterns of metabolic processes . One of the important characteristics of this bacterial family is lactose breakdown (presence of the lac operon). The lac operon includes the genes lacZ (codes for b-galactosidase), lacY (codes for b-galactoside permease), and lacA (codes for transacetylase). Lactose-positive Enterobacteriaceae are grouped together as coliform Enter- obacteriaceae. Salmonellae and most of the shigellae are lactose-negative.
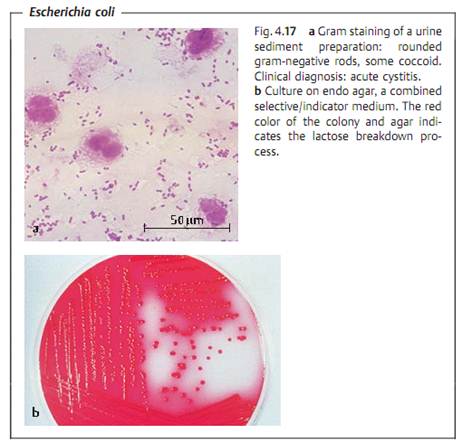
Morphology and culture. Enterobacteriaceae are short Gram-negative rods with rounded ends, 0.5-1.5 µm thick, and 24 µm long (Fig. 4.17a). Many have peritrichous flagellation. Species with many flagella (e.g., Proteus species) show motility on the agar surface, which phenomenon is known as “swarming.” Some Enterobacteriaceae possess a capsule.
All bacteria in this family can readily be cultured on simple nutrient mediums. They are rapidly growing facultative anaerobes. Their mean generation time in vitro is 20-30 minutes. They show resistance to various chemicals (bile salts, crystal violet), which fact is made use of in selective culturing. Endo agar is an important selective indicator medium; it allows only Gram-negative rod bacteria to grow and indicates lactose breakdown (Fig. 4.17b).
Antigen structure. The most important antigens of the Enterobacteriaceae are:
- O antigens. Specific polysaccharide chains in the lipopolysaccharide complex of the outer membrane (p. 156).
- H antigens. Flagellar antigens consisting of protein.
- K antigens. Linear polymers of the outer membrane built up of a repeated series of carbohydrate units (sometimes proteins as well). They can cover the cell densely and render them O inagglutinable .
- F antigens. Antigens of protein attachment fimbriae.
Pathogenicity determinants. A number of factors are known to play a role in the pathogenicity of various Enterobacteriaceae infections. The most important are:
- Adhesion factors. Attachment fimbriae, attachment pili, colonizing factor antigens (CFAs).
- Invasive factors. Proteins localized in the outer membrane (invasins) that facilitate the invasion of target cells.
- Exotoxins.
* Enterotoxins disturb the normal functioning of enterocytes. Stimulation of adenylate or guanylate cyclase; increased production of cAMP . This results in the loss of large amounts of electrolytes and water.
* Cytotoxins exert a direct toxic effect on cells (enterocytes, endothelial cells).
- Endotoxin. Toxic effect of lipoid A as a component of LPS .
- Serum resistance. Resistance to the membrane attack complex C5b6789 of the complement system .
- Phagocyte resistance. Makes survival in phagocytes possible. Resistance against defensins and/or oxygen radicals .
- Cumulation of Fe2+. Active transport of Fe2+ by siderophores in the bacterial cell .
 الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
الاكثر قراءة في البكتيريا
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















