

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci
المؤلف:
Cornelissen, C. N., Harvey, R. A., & Fisher, B. D
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Microbiology
الجزء والصفحة:
3rd edition , p76-77
2025-02-19
477
Of 12 coagulase-negative staphylococcal species that have been recovered as normal commensals of human skin and anterior nares, the most abundant and important is S. epidermidis. For this reason some clinical laboratories designate all coagulase-negative staphylococci as S. epidermidis, a practice that is not encouraged. The second most important coagulase-negative staphylococcus is S. saprophyticus, which has a special medical niche. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal species are important agents of hospital-acquired infections associated with the use of implanted prosthetic devices and catheters.
A. Staphylococcus epidermidis
S. epidermidis is present in large numbers as part of the normal flora of the skin . As such, it is frequently recovered from blood cultures, generally as a contaminant from skin. Despite its low virulence, it is a common cause of infection of implants such as heart valves and catheters (Figure 1). Acquired drug resistance by S. epidermidis is even more frequent than by S. aureus. Vancomycin sensitivity remains the rule, but vancomycin-resistant isolates have been reported. S. epidermidis produces an extracellular polysaccharide material called polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (sometimes called “slime”), that facilitates adherence to bioprosthetic material surfaces, such as intravenous catheters, and acts as a barrier to antimicrobial agents.

Fig1. Staphylococcus epidermidis attached by its biofilm and growing on the surface of a cathether.
B. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
This organism is a frequent cause of cystitis in women, probably related to its occurrence as part of normal vaginal flora . It tends to be sensitive to most antibiotics, even penicillin G. S. saprophyticus can be distinguished from S. epidermidis and most other coagulase-negative staphylococci by its natural resistance to novobiocin (Figure 2). [Note: Urinary coagulase-negative staphylococcus is often presumed to be S. saprophyticus; but novobiocin resistance can be used for confirmation.]. Figure 3 presents a summary of diseases caused by staphylococci.
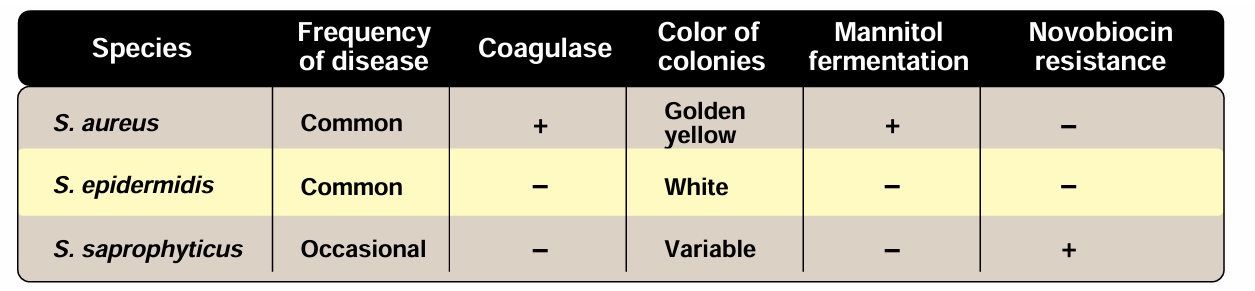
Fig2. Summary of various species of staphylococci.
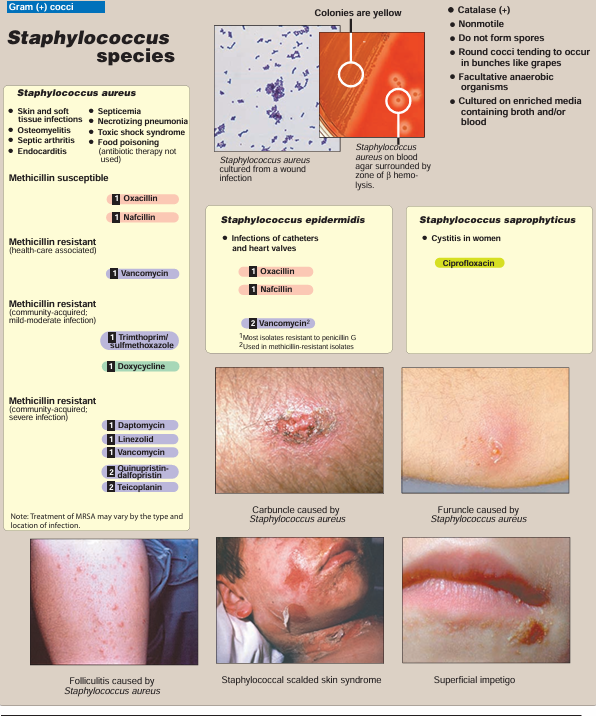
Fig3. Summary of staphylococcal disease. 1 Indicates first-line drugs; 2 indicates alternative drugs.