

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Thyroid Gland
المؤلف:
Marieb, Elaine Nicpon
المصدر:
Human Anatomy and Physiology
الجزء والصفحة:
1-11-2015
1594
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland, the largest of the endocrine glands, is located in the neck just below the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It consists of two lobes, one on either side of the trachea, joined by a narrow band or isthmus. It is composed of numerous hollow ball-shaped follicles with small, interspersed clusters of parafollicular cells.
Follicle cells concentrate and attach iodine to the amino acid tyrosine, producing two forms of thyroid hormone (TH): thyroxine or tetraiodothy- ronine (T4), and smaller amounts of triiodothyronine (T3). Manufacture and release of these hormones into the blood is regulated by thyroid stimulating hormone, TSH, from the pituitary gland. The major effect of TH is to stimulate activity of enzymes involved in energy production through the oxidation (burning) of glucose, thus increasing basal metabolic rate. A side effect of this increased activity is the production of body heat.
Overactivity of the thyroid gland, called hyperthyroidism, causes elevated metabolic rate, nervousness, and weight loss. The most common form of hyperthyroidism, Graves’ disease, is an autoimmune disease; it is accompanied by swelling of the thyroid (goiter) and bulging of the eyes (exophthalmos). Adult hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, causes myxedema, characterized by lowered metabolic rate, sluggishness, and weight gain. Additional consequences of low TH levels in infants are stunted growth and irreversible brain damage. Hypothyroidism resulting from low iodine intake, with consequent low TH manufacture, produces an enlargement of the thyroid gland called endemic goiter. TSH is responsible for this enlargement.
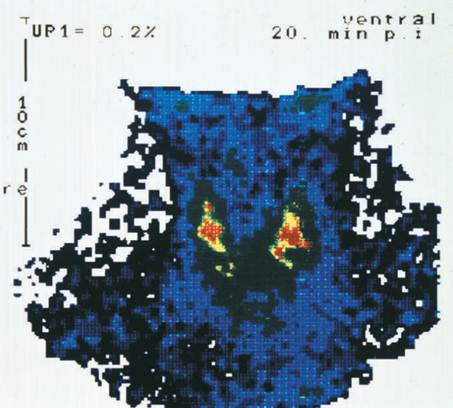
A color-enchanced scintigram (gamma scan) of a human thyroid gland.
Parafollicular cells produce the hormone calcitonin, which lowers blood calcium levels by suppressing the activity of bone-destroying cells called osteoclasts, and stimulating calcium uptake by bones. Calcitonin is important in children, where growing bones are being constantly remodeled. It has little effect on the normal adult skeleton, but may be prescribed in nasal spray form to help reduce bone destruction in osteoporosis. Parathormone, produced by the parathyroid gland, has opposing effects on blood calcium levels.
References
Marieb, Elaine Nicpon. Human Anatomy and Physiology, 5th ed. Boston: Addison-Wes- ley-Longman, 2001.
Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, 2nd ed. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2001.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الغدد
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الغدد
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















