

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Parasitic Diseases
المؤلف:
Cheng, Thomas C
المصدر:
General Parasitology
الجزء والصفحة:
27-10-2015
2712
Parasitic Diseases
A parasite is typically an organism that lives in or on the body of another living organism, the host, and harms it by feeding on its tissues or stealing nutrients. In the broad sense, parasites include certain bacteria, fungi, protozoans, worms, arthropods, and a few vertebrates. Bacterial, fungal, and protozoan diseases are discussed elsewhere in this encyclopedia. This article focuses on a few human diseases caused by parasitic worms and arthropods.
The worms that infect humans include trematodes (flukes), cestodes (tapeworms), and nematodes (roundworms). One of the most serious trematode diseases is schistosomiasis, caused by three species in the genus Schistosoma. Schistosomes, or blood flukes, live in blood vessels of the urinary bladder and intestines. They lay eggs that digest their way through the blood vessel and the bladder or intestinal wall, and thus find their way into the urine or feces.
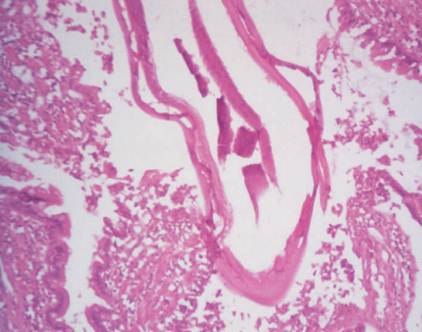
Hookworms (fuschia stain) in a dog's small intestine. Thousands of hookworks may attach to the wall of the small intestine, sucking so much blood that they make the victim severely anemic.
When discharged into fresh water, they hatch and produce a swimming larva, the miracidium, which infects a snail. Later, another larva called the cercaria emerges from the snail and penetrates the skin of people who come in contact with the water. Eggs lodged in the human intestine or bladder, or washed by the bloodstream into the liver, cause an intense allergic reaction that leads to degeneration of these organs and often death of the victim.
Cestodes in general are less pathogenic (disease-producing) than trema- todes. However, the fish tapeworm, Diphyllobothrium latum, can cause severe anemia by robbing the human host of vitamin B12. The pork tapeworm, Taenia solium, can cause intestinal obstruction and produces eggs that sometimes hatch in the human body, leading to larval invasion of the muscles, brain, lungs, heart, and other organs. Echinococcus granulosus, a tapeworm of dogs and wolves, sometimes infects humans when a dog licks a person in the face. It does not mature in humans, but its larvae can produce hydatid cysts, ranging from grape-sized to grapefruit-sized, in the liver, brain, and lungs, with fatal results.
Among the most widespread nematode infections of humans is hookworm disease, caused by Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale. Hookworms are only 1 centimeter (0.4 inch) long, but thousands of them may attach to the wall of the small intestine, collectively sucking so much blood that they make a person severely anemic and stunt the victim’s growth and mental development.
Onchocerca volvulus, a nematode transmitted by the bites of blackflies, produces larvae that migrate through the cornea of the human eye. In parts of Latin America and Africa, it blinds many people before middle age. Blackflies breed in flowing waters, and this disease is therefore called river blindness.
The major parasitic arthropods of humans are mites, ticks, fleas, lice, mosquitoes, and blood-sucking flies. In themselves, these parasites usually cause little more than irritation, although it can be intense. More seriously, however, they act as vectors—agents that transmit pathogenic viruses, bacteria, and protozoans. Millions of people have died in great epidemics of plague, transmitted by fleas, and typhus, transmitted by body lice. Malaria, transmitted by mosquitoes, remains one of the world’s greatest killers and most stubborn public health problems today.
Any parasitology textbook can provide further details on these and related parasites, how they infect humans, mechanisms of disease, and how to control or avoid them. Parasitic arthropods are also covered by books on medical entomology.
References
Cheng, Thomas C. General Parasitology, 2nd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, 1986.
Harwood, Robert F., and Maurice T. James. Entomology in Human and Animal Health, 7th ed. New York: Macmillan, 1979.
Schmidt, Gerald D., and Larry S. Roberts. Foundations of Parasitology, 6th ed. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2000.
Zinsser, Hans. Rats, Lice, and History. Boston: Little, Brown, 1963.
 الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















