

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Deoxyribonucleotide Synthesis
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
17-11-2021
2545
Deoxyribonucleotide Synthesis
The nucleotides described thus far all contain ribose (ribonucleotides). DNA synthesis, however, requires 2′-deoxyribonucleotides, which are produced from ribonucleoside diphosphates by the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase during the S-phase of the cell cycle . [Note: The same enzyme acts on pyrimidine ribonucleotides.]
A. Ribonucleotide reductase
Ribonucleotide reductase (ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase) is a dimer composed of two nonidentical subunits, R1 (or, α) and the smaller R2 (or, β), and is specific for the reduction of purine nucleoside diphosphates (ADP and GDP) and pyrimidine nucleoside diphosphates (CDP and UDP) to their deoxy forms (dADP, dGDP, dCDP, and dUDP). The immediate donors of the hydrogen atoms needed for the reduction of the 2′-hydroxyl group are two sulfhydryl (–SH) groups on the enzyme itself (R1 subunit), which form a disulfide bond during the reaction ). [Note: R2 contains the stable tyrosyl radical required for catalysis at R1.]
1. Reduced enzyme regeneration: In order for ribonucleotide reductase to continue to produce deoxyribonucleotides at R1, the disulfide bond created during the production of the 2′-deoxy carbon must be reduced.
The source of the reducing equivalents is thioredoxin, a protein coenzyme of ribonucleotide reductase. Thioredoxin contains two cysteine residues separated by two amino acids in the peptide chain. The two –SH groups of thioredoxin donate their hydrogen atoms to ribonucleotide reductase, forming a disulfide bond in the process (Fig. 1).
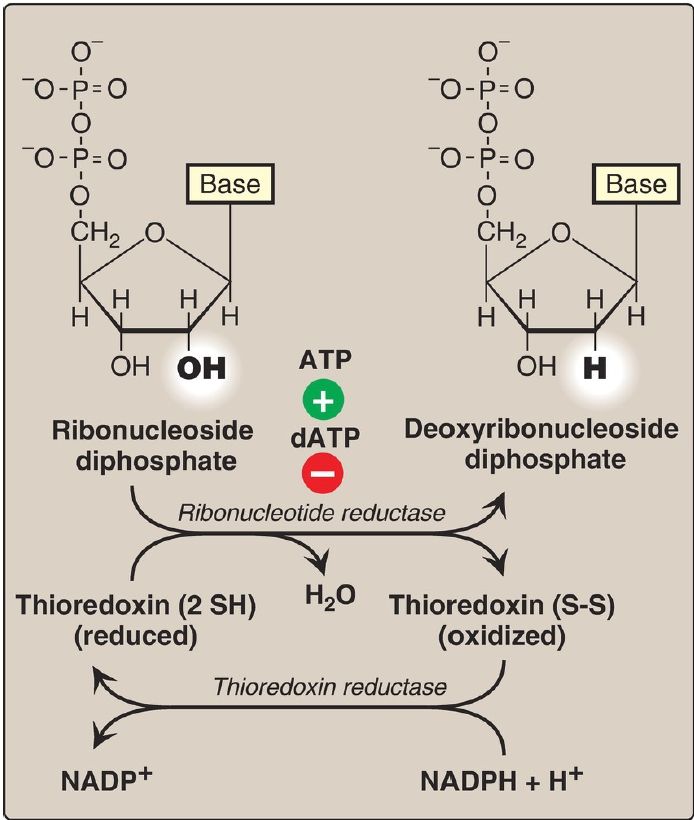
Figure 1: Conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides. NADP(H) = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; dATP = deoxyadenosine triphosphate.
2. Reduced thioredoxin regeneration: Thioredoxin must be converted back to its reduced form in order to continue performing its function. The reducing equivalents are provided by NADPH + H+, and the reaction is catalyzed by thioredoxin reductase, a selenoprotein .
B. Deoxyribonucleotide synthesis regulation
Ribonucleotide reductase is responsible for maintaining a balanced supply of the deoxyribonucleotides required for DNA synthesis. Consequently, the regulation of the enzyme is complex. In addition to the catalytic site, R1 contains two distinct allosteric sites involved in regulating enzymic activity (Fig. 2).

Figure 2: Regulation of ribonucleotide reductase. dATP, dTTP, and dGTP = deoxyadenosine, deoxythymidine, and deoxyguanosine triphosphates. [Note: The R1 subunit is also referred to as α and the R2 as β.]
1. Activity sites: The binding of dATP to allosteric sites (known as activity sites) on R1 inhibits the overall catalytic activity of the enzyme and, therefore, prevents the reduction of any of the four nucleoside diphosphates. This effectively prevents DNA synthesis and explains the toxicity of increased levels of dATP seen in conditions such as adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency . In contrast, ATP bound to these sites activates the enzyme.
2. Substrate specificity sites: The binding of nucleoside triphosphates to additional allosteric sites (known as substrate specificity sites) on R1 regulates substrate specificity, causing an increase in the conversion of different species of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides as they are required for DNA synthesis. For example, deoxythymidine triphosphate binding at the specificity site causes a conformational change that allows reduction of GDP to dGDP at the catalytic site when ATP is at the
activity site.
The drug hydroxyurea (hydroxycarbamide) inhibits ribonucleotide reductase, thereby inhibiting the generation of substrates for DNA synthesis. The drug is an antineoplastic agent and is used in the treatment of cancers such as melanoma. Hydroxyurea is also used in the treatment of sickle cell anemia . However, the increase in fetal hemoglobin seen with hydroxyurea is because of changes in gene expression and not to ribonucleotide reductase inhibition.