

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Phosphatidylinositol
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
15-10-2021
2723
Phosphatidylinositol
PI is synthesized from free inositol and CDP-DAG, as shown in Figure 1. PI is an unusual phospholipid in that it most frequently contains stearic acid on carbon 1 and arachidonic acid on carbon 2 of the glycerol.
Therefore, PI serves as a reservoir of arachidonic acid in membranes and, thus, provides the substrate for prostaglandin synthesis when required. Like PS, PI has a net negative charge. [Note: There is asymmetry in the phospholipid composition of the cell membrane. PS and PI, for example, are found primarily on the inner leaflet. Asymmetry is achieved by ATP-dependent enzymes known as “flippases” and “floppases.”]
1. Role in signal transduction across membranes: The phosphorylation of membrane-bound PI produces polyphosphoinositides such as phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate ([PIP2]; Fig. 1). The cleavage of PIP2 by phospholipase C occurs in response to the binding of various neurotransmitters, hormones, and growth factors to G protein–coupled receptors (GPCR), such as the α1 adrenergic receptor, on the cell membrane and activation of the Gq α-subunit (Fig. 2). The products of this cleavage, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and DAG, mediate the mobilization of intracellular calcium and the activation of protein kinase C, which act synergistically to evoke specific cellular responses. Signal transduction across the membrane is, thus, accomplished.
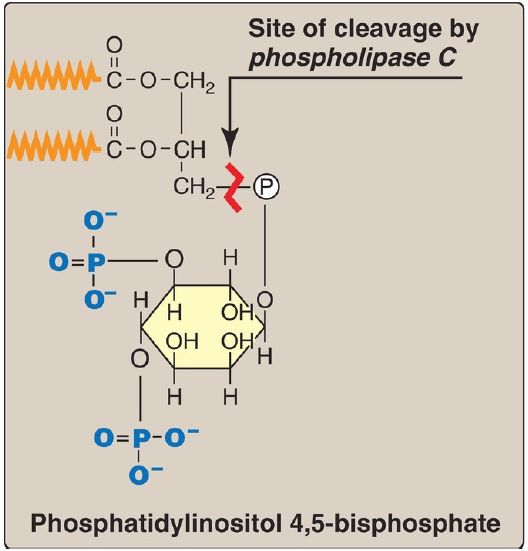
Figure 1: Structure of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). Cleavage by phospholipase C produces inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol. ( is a fatty acid hydrocarbon chain.) = phosphate.
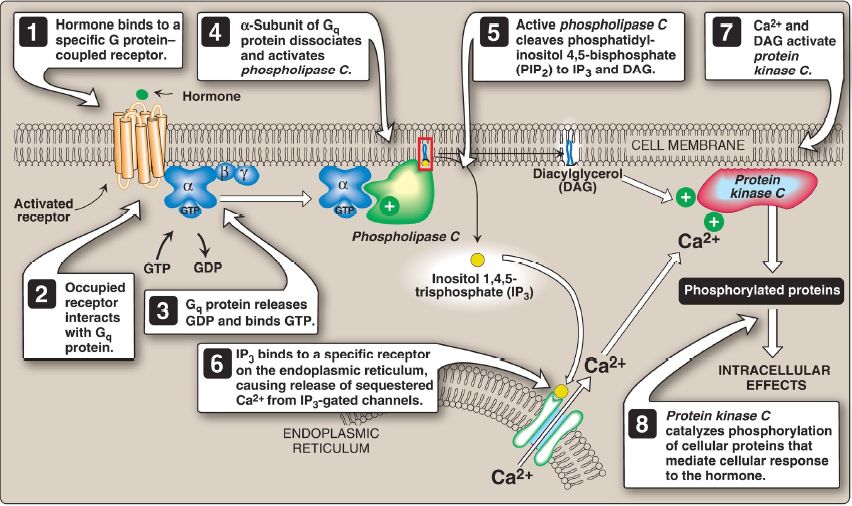
Figure 2: Role of inositol triphosphate and diacylglycerol in cell signaling. GDP and GTP = guanosine di- and triphosphates; Ca2+ = calcium.
2. Role in membrane protein anchoring: Specific proteins can be covalently attached through a carbohydrate bridge to membrane-bound PI (Fig. 3). For example, lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme that degrades triacylglycerol in lipoprotein particlesis attached to capillary endothelial cells by a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. [Note: GPI-linked proteins are also found in a variety of parasitic protozoans, such as trypanosomes and leishmania.] Being attached to a membrane lipid (rather than being an integral part of the membrane) allows GPI-anchored proteins increased lateral mobility on the extracellular surface of the plasma membrane. The protein can be cleaved from its anchor by the action of phospholipase C (see Fig. 3).
[Note: A deficiency in the synthesis of GPI in hematopoietic cells results in the hemolytic disease paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, because GPI-anchored proteins protect blood cells from complement-mediated lysis.]
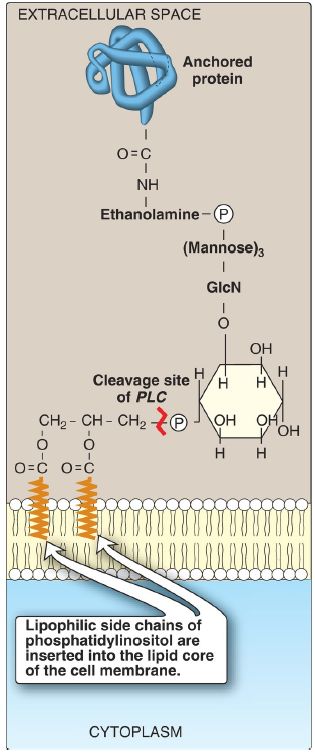
Figure 3: Example of a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) membrane protein anchor. GlcN = glucosamine; = phosphate; PLC = phospholipase C.