

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Structure of the Wittig reagent
المؤلف:
University of Missouri System
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry ii
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
12-10-2020
2815
Structure of the Wittig reagent
One of the simplest ylides is methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). The Wittig reagent may be written in the phosphorane form or the ylide form:

The ylide form is a significant contributor, and the carbon is nucleophilic. It has been noted that dipolar phosphorus compounds are stabilized by p-d bonding. This bonding stabilization extends to carbanions adjacent to phosphonium centers. An ylide is defined as a compound with opposite charges on adjacent atoms, both of which have complete octets.
Reactivity
Simple phosphoranes (Wittig reagents) are reactive towards air and water, so they are usually handled under nitrogen. These will react easily with most aldehydes and ketones.
However, phosphoranes some are stabilized by electron-withdrawing groups, as in Ph3P=CHCO2R and Ph3P=CHPh. These ylides are sufficiently stable to be sold commercially

From the phosphonium salts, these reagents are formed more readily, requiring only a moderate base such as NaOH, and they are usually more air-stable. Stabilized Wittig reagents are less reactive than simple ylides, and so they usually fail to react with ketones, and they usually give rise to an E-alkene product when they react, rather than the more usual Z-alkene.
The Wittig reagent itself is usually made from a primary alkyl halide via an SN2 reaction. The SN2 reaction of triphenylphosphine with most secondary halides is inefficient. For this reason, Wittig reagents are rarely used to prepare tetrasubstituted alkenes. However, the Wittig reagent can tolerate many other variants. It may contain alkenes and aromatic rings, and it is compatible with ethers and even ester groups. Even C=O and nitrile groups can be present if conjugated with the ylide- these are the stabilized ylides mentioned above.
Examples of the Wittig reaction



Because of its reliability and wide applicability, the Wittig reaction has become a standard tool for synthetic organic chemists. A principal advantage of alkene synthesis by the Wittig reaction is that the location of the double bond is absolutely fixed, in contrast to the mixtures often produced by classical E1 or E2 elimination reactions.
The most popular use of the Wittig reaction is for the introduction of a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). Using this reagent even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative (see example above).
Exercises
1) Please write the product of the following reactions.

2) Please indicate the starting material required to produce the product.

3) Please draw the structure of the oxaphosphetane which is made during the mechanism of the reaction given that produces product C.
4) Please draw the structure of the betaine which is made during the mechanism of the reaction given that produces product D.
5) Please give a detailed mechanism and the final product of this reaction

6) It has been shown that reacting and epoxide with triphenylphosphine forms an alkene. Please propose a mechanism for this reaction. Review the section on epoxide reactions if you need help.

1)

2)

3)

4)

5)
Nucleophillic attack on the carbonyl

Formation of a 4 membered ring

Formation of the alkene

6) Nucleophillic attack on the epoxide
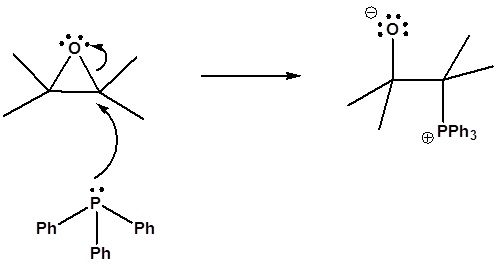
Formation of a 4 membered ring

Formation of the alkene

 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















