


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 17-1-2020
Date: 8-1-2020
Date: 20-1-2020
|
Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes
Ethylene and propylene, the simplest alkenes, are the two most important organic chemicals produced industrially. Approximately 127 million metric tons of ethylene and 54 million metric tons of propylene are produced worldwide each year for use in the synthesis of polyethylene, polypropylene, ethylene glycol, acetic acid, acetaldehyde, and a host of other substances (Figure 1-1).
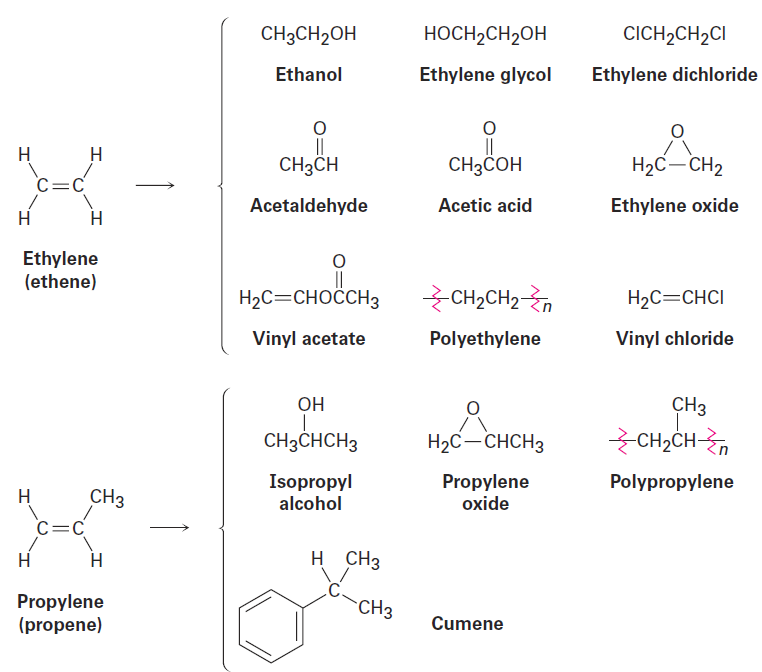
Figure 1-1 Compounds derived industrially from ethylene and propylene.
Ethylene, propylene, and butene are synthesized industrially by steam cracking of light (C2–C8) alkanes.
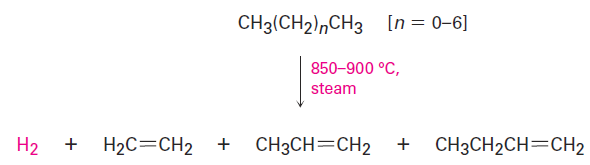
Steam cracking takes place without a catalyst at temperatures up to 900 °C. The process is complex, although it undoubtedly involves radical reactions. The high-temperature reaction conditions cause spontaneous homolytic breaking of C- C and C- H bonds, with resultant formation of smaller fragments. We might imagine, for instance, that a molecule of butane splits into two ethyl radicals, each of which then loses a hydrogen atom to generate two molecules of ethylene.
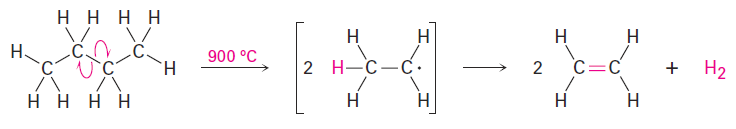
Steam cracking is an example of a reaction whose energetics are dominated by entropy (ΔS°) rather than by enthalpy (ΔH°) in the free-energy equation ΔG° =ΔH° - TΔS°. Although the bond dissociation energy Δ for a carbon–carbon single bond is relatively high (about 370 kJ/mol) and cracking is endothermic, the large positive entropy change resulting from the fragmentation of one large molecule into several smaller pieces, together with the high temperature, makes the TΔS° term larger than the ΔH° term, thereby favoring the cracking reaction.



|
|
|
|
"إنقاص الوزن".. مشروب تقليدي قد يتفوق على حقن "أوزيمبيك"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين تحقق اختراقا بطائرة مسيرة مزودة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتب السيد السيستاني يعزي أهالي الأحساء بوفاة العلامة الشيخ جواد الدندن
|
|
|