


 7:50:19
7:50:19  2018-10-10
2018-10-10  1670
1670
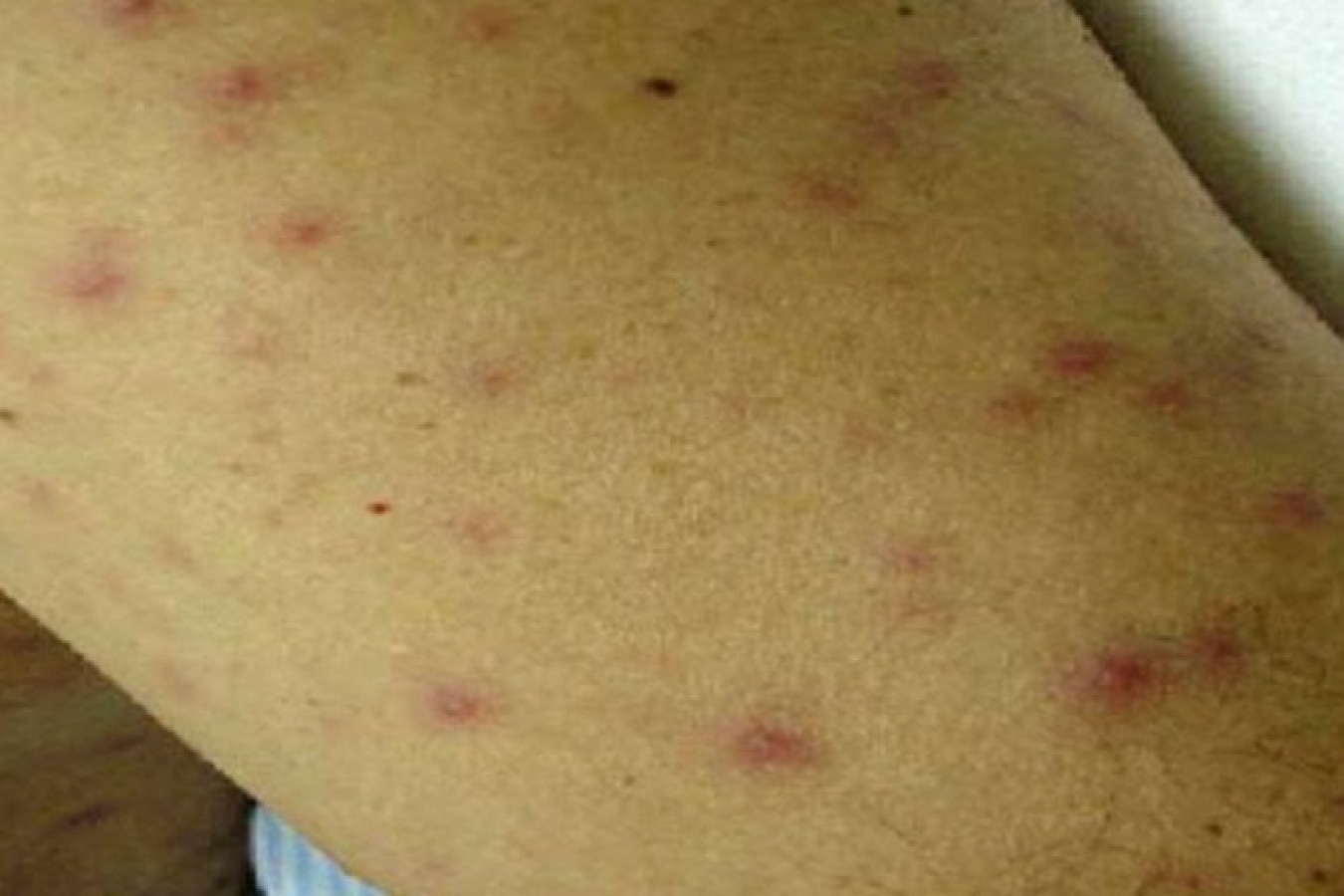
Typhus is a disease caused by infection with one or more rickettsial bacteria. Fleas, mites (chiggers), lice, or ticks transmit it when they bite you. Fleas, mites, lice, and ticks are types of invertebrate animals known as arthropods. When arthropods carrying around rickettsial bacteria bite someone, they transmit the bacteria that causes typhus. Scratching the bite further opens the skin and allows the bacteria greater access to the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, the bacteria continue to reproduce and grow.
There are three different types of typhus:
The type of typhus you are infected with depends on what bit you. Arthropods are typically carriers of a typhus strain unique to their species.
Typhus outbreaks usually only occur in developing countries or in regions of poverty, poor sanitation, and close human contact. Typhus is generally not a problem in the United States, but you may become infected while traveling abroad.
Untreated typhus can lead to serious complications, and it’s potentially fatal. It’s important to see your doctor if you suspect that you may have typhus.
Cause of typhus
Typhus is not transmitted from person to person like a cold or the flu. There are three different types of typhus, and each type is caused by a different type of bacterium and transmitted by a different type of arthropod.
Epidemic/louse-borne typhus
This type is caused by Rickettsia prowazekii and carried by the body louse, and possibly by ticks as well. It can be found around the world, including in the United States, but is typically found in areas of high population and poor sanitation, where conditions promote lice infestation.
Endemic typhus
Alternatively known as murine typhus, this type is caused by Rickettsia typhi and is carried by the rat flea or cat flea. Endemic typhus can be found worldwide. It may be found among people in close contact with rats. It isn’t commonly found in the United States, but cases have been reported in some areas, primarily Texas and southern California.
Scrub typhus
This type is caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi and carried by mites in their larval stage when they are chiggers. This type of typhus is more commonly found in Asia, Australia, Papua New Guinea, and the Pacific Islands. It’s also called tsutsugamushi disease.
The louse, flea, tick, or mite becomes a carrier of the bacteria when they feed on the blood of an infected person (epidemic typhus) or an infected rodent (any of the three typhus forms mentioned above).
If you come in contact with these bacterium-carrying arthropods (for example, by sleeping on bed sheets infested with lice), you can become infected in a couple ways. The bacteria, in addition to being transmitted through your skin by their bites, can also be transmitted through their feces. If you scratch the skin over an area where lice or mites have been feeding, the bacteria in their feces can enter your bloodstream through the tiny wounds on your skin.
Symptoms of typhus
Symptoms vary slightly by the type of typhus, but there are symptoms that are associated with all three types of typhus, such as:
Symptoms of epidemic typhus usually appear suddenly and include:
The symptoms of endemic typhus last for 10 to 12 days and are very similar to the symptoms of epidemic typhus but are usually less severe. They include:
Symptoms seen in people with scrub typhus include:
Diagnosing typhus
If you suspect that you have typhus, your doctor will ask about your symptoms and your medical history. To help with the diagnosis, tell your doctor if you:
Diagnosis is difficult because symptoms are common to other infectious diseases, including:
Diagnostic tests for the presence of typhus include:
Treatment for typhus
Antibiotics most commonly used to treat typhus include:
Outlook for typhus
Early treatment with antibiotics is very effective, and relapses aren’t common if you take the full course of antibiotics. Delayed treatment and misdiagnosis can lead to a more severe case of typhus.
Epidemics of typhus are more common in poor, unsanitary, and crowded areas. People who are most at risk of dying are generally those who are unable to afford quick treatments. The overall mortality rate for untreated typhus depends on the type of typhus and other factors, such as age and overall health status.
The highest rates are seen in the older adults and those who are malnourished. Children usually recover from typhus. People with underlying diseases (such as diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, or chronic renal disorders) also have a higher risk of mortality. Mortality for epidemic typhus that goes untreated can range from 10 to 60 percent, and mortality from untreated scrub typhus can range up to 30 percent.
Preventing typhus
During World War II, a vaccine was created to prevent epidemic typhus. However, the shrinking number of cases has stopped the manufacture of the vaccine. The easiest way to prevent typhus is by avoiding the pests that spread it.
Suggestions for prevention include:
Use tick, mite, and insect repellant. Perform routine examinations for ticks, and wear protective clothing if you’re traveling near an area where there have been typhus outbreaks.
Reality Of Islam |
|

Researchers

A well-know

Scientists

As AI-power
 9:3:43
9:3:43
 2018-11-05
2018-11-05
10 benefits of Marriage in Islam
 7:5:22
7:5:22
 2019-04-08
2019-04-08
benefits of reciting surat yunus, hud &
 9:45:7
9:45:7
 2018-12-24
2018-12-24
advantages & disadvantages of divorce
 11:35:12
11:35:12
 2018-06-10
2018-06-10
 6:0:51
6:0:51
 2018-10-16
2018-10-16
 9:30:2
9:30:2
 2021-11-12
2021-11-12
 2:13:43
2:13:43
 2022-05-27
2022-05-27
 2:42:26
2:42:26
 2023-02-02
2023-02-02
 1:38:41
1:38:41
 2021-12-08
2021-12-08
 7:32:24
7:32:24
 2022-02-14
2022-02-14
 5:58:12
5:58:12
 2021-12-18
2021-12-18
 3:43:50
3:43:50
 2022-11-05
2022-11-05
 5:41:46
5:41:46
 2023-03-18
2023-03-18
| LATEST |